Common variable immunodeficiency with granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease and preceding neurological involvement: a case-report
- PMID: 32736614
- PMCID: PMC7393898
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-020-01231-6
Common variable immunodeficiency with granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease and preceding neurological involvement: a case-report
Abstract
Background: Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is a group of heterogeneous primary immunodeficiencies characterised by a dysregulated and impaired immune response. In addition to an increased susceptibility to infection, it is also associated with noninfectious autoimmune and lymphoproliferative complications. CVID is rarely associated with neurological complications. Pulmonary involvement is more common, and patients can develop an interstitial lung disease known as granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD).
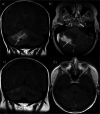
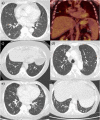
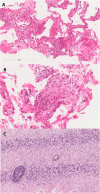
Case presentation: A 50-year-old Caucasian female with a history of Evans syndrome (idiopathic thrombocytopaenic purpura and autoimmune haemolytic anaemia) and hypogammaglobulinaemia initially presented to the neurology clinic with marked cerebellar ataxia and headaches. Following extensive investigation (which included brain biopsy), she was diagnosed with neuro-sarcoidosis and her symptoms resolved following treatment with immunosuppressive therapy. Over the following 10 years, she was extensively investigated for recurrent pulmonary infections and abnormal radiological findings, which included pulmonary nodules, infiltrates and splenomegaly. Subsequently, she was referred to an immunology clinic, where immunoglobulin replacement treatment was started for what was ultimately considered to be CVID. Shortly afterwards, evaluation of her clinical, radiological and histological findings at a specialist interstitial lung disease clinic led to a diagnosis of GLILD.
Conclusion: CVID is a condition which should be suspected in patients with immunodeficiency and recurrent infections. Concomitant autoimmune disorders such as haemolytic anaemia and immune thrombocytopenia may further support the diagnosis. As illustrated in this case, there is a rare association between CVID and inflammatory involvement of the neurological system. Respiratory physicians should also suspect CVID with associated GLILD in patients with apparent pulmonary granulomatous disease and recurrent infections. In addition, this case also highlights the challenge of diagnosing CVID and its associated features, and how the definitive exclusion of other pathologies such as malignancy, mycobacterial infection and lymphoma is required as part of this diagnostic process.
Keywords: Common variable immunodeficiency; Granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease; Sarcoidosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease as the first manifestation of common variable immunodeficiency.Clin Respir J. 2018 Jan;12(1):337-343. doi: 10.1111/crj.12511. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Clin Respir J. 2018. PMID: 27243233
-
Granulomatous Lymphocytic Interstitial Lung Disease (GLILD) in Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID): A Multicenter Retrospective Study of Patients From Italian PID Referral Centers.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 10;12:627423. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.627423. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33777011 Free PMC article.
-
Common variable immunodeficiency and its inflammatory neurological manifestations: A case report and literature review.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022 Nov;67:104086. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2022.104086. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022. PMID: 35985210 Review.
-
Sarcoidosis and common variable immunodeficiency: similarities and differences.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2014 Jun;35(3):330-5. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1376862. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 25007085 Review.
-
An 18-year-old woman with Kabuki syndrome, immunoglobulin deficiency and granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease.Conn Med. 2012 Jan;76(1):15-8. Conn Med. 2012. PMID: 22372173
Cited by
-
The Importance of the Transcription Factor Foxp3 in the Development of Primary Immunodeficiencies.J Clin Med. 2022 Feb 11;11(4):947. doi: 10.3390/jcm11040947. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35207219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sarcoidosis: Pitfalls and Challenging Mimickers.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jan 11;7:594275. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.594275. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33505980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sarcoidosis versus Granulomatous and Lymphocytic Interstitial Lung Disease in Common Variable Immunodeficiency: A Comparative Review.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 6;12(7):1503. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071503. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic testing for interstitial lung disease in common variable immunodeficiency: a systematic review.Front Immunol. 2023 May 8;14:1190235. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1190235. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37223103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geha RS, Notarangelo LD, Casanova JL, et al. Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an update from the International Union of Immunological Societies Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases Classification Committee. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120(4):776–794. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.08.053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

