A neurovascular high-frequency optical coherence tomography system enables in situ cerebrovascular volumetric microscopy
- PMID: 32737314
- PMCID: PMC7395105
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-17702-7
A neurovascular high-frequency optical coherence tomography system enables in situ cerebrovascular volumetric microscopy
Abstract
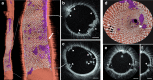
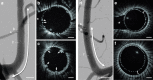
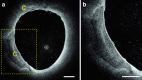
Intravascular imaging has emerged as a valuable tool for the treatment of coronary and peripheral artery disease; however, no solution is available for safe and reliable use in the tortuous vascular anatomy of the brain. Endovascular treatment of stroke is delivered under image guidance with insufficient resolution to adequately assess underlying arterial pathology and therapeutic devices. High-resolution imaging, enabling surgeons to visualize cerebral arteries' microstructure and micron-level features of neurovascular devices, would have a profound impact in the research, diagnosis, and treatment of cerebrovascular diseases. Here, we present a neurovascular high-frequency optical coherence tomography (HF-OCT) system, including an imaging console and an endoscopic probe designed to rapidly acquire volumetric microscopy data at a resolution approaching 10 microns in tortuous cerebrovascular anatomies. Using a combination of in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo models, the feasibility of HF-OCT for cerebrovascular imaging was demonstrated.
Conflict of interest statement
G.J.U., L.M.P., and B.H.D. are employees of Gentuity LLC and hold stocks. M.G.M. is a consultant on a fee-per-hour basis for InNeuroCo In and Stryker Neurovascular. D.K.L. has received research support from Medtronic Neurovascular. M.J.G. has received research support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the United States–Israel Binational Science Foundation, Anaconda, Apic Bio, Arsenal Medical, Axovant, Cerenovus, Ceretrieve, Cook Medical, Galaxy LLC, Gentuity, Imperative Care, InNeuroCo, Insera, Magneto, Microvention, Medtronic Neurovascular, MIVI Neurosciences, Neuravi, Neurogami, Philips Healthcare, Progressive Neuro, Rapid Medical, Route 92 Medical, Stryker Neurovascular, Syntheon, and the Wyss Institute; is a consultant on a fee-per-hour basis for Cerenovus, Imperative Care, Medtronic Neurovascular, Mivi Neurosciences, Phenox, Route 92 Medical, and Stryker Neurovascular; holds stock in Imperative Care, InNeuroCo, and Neurogami. A.S.P. has been a proctor on a fee-per-hour basis for Stryker Neurovascular, and Cerenovus; has research grants from Cerenovus, Medtronic Neurovascular, and Stryker Neurovascular; holds stock in InNeuroCo, and NTI. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Neuroendovascular optical coherence tomography imaging and histological analysis.Neurosurgery. 2011 Aug;69(2):430-9. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e318212bcb4. Neurosurgery. 2011. PMID: 21358358 Free PMC article.
-
Natural history and surgical treatment of occlusive cerebrovascular disease evaluated by serial arteriography.Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1968 Sep;104(1):1-17. doi: 10.2214/ajr.104.1.1. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1968. PMID: 5672766 No abstract available.
-
Evaluation of cerebral artery perforators and the pipeline embolization device using optical coherence tomography.J Neurointerv Surg. 2012 Jul;4(4):291-4. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2011-010102. Epub 2011 Sep 20. J Neurointerv Surg. 2012. PMID: 21990536
-
Intracranial vascular lesions and anatomical variants all residents should know.Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2010 May-Jun;39(3):91-109. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2009.07.005. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2010. PMID: 20307787 Review.
-
[Transcranial Doppler ultrasound].Can Assoc Radiol J. 1991 Dec;42(6):389-96. Can Assoc Radiol J. 1991. PMID: 1751900 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Optical Coherence Tomography in Cerebrovascular Disease: Open up New Horizons.Transl Stroke Res. 2023 Apr;14(2):137-145. doi: 10.1007/s12975-022-01023-6. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Transl Stroke Res. 2023. PMID: 35445969 Review.
-
Preface to the special issue on "Biomedical Optics".Front Optoelectron. 2020 Dec;13(4):305-306. doi: 10.1007/s12200-020-1132-x. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Front Optoelectron. 2020. PMID: 36641570 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Phenotyping calcification in vascular tissues using artificial intelligence.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 17:arXiv:2401.07825v2. ArXiv. 2024. PMID: 38313202 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
High-resolution image-guided WEB aneurysm embolization by high-frequency optical coherence tomography.J Neurointerv Surg. 2021 Jul;13(7):669-673. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-016447. Epub 2020 Sep 28. J Neurointerv Surg. 2021. PMID: 32989033 Free PMC article.
-
Portable, handheld, and affordable blood perfusion imager for screening of subsurface cancer in resource-limited settings.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jan 11;119(2):e2026201119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2026201119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 34983869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becske T, et al. Pipeline for uncoilable or failed aneurysms: results from a multicenter clinical trial. Radiology. 2013;267:858–868. - PubMed
-
- Heller R, Calnan DR, Lanfranchi M, Madan N, Malek AM. Incomplete stent apposition in Enterprise stent-mediated coiling of aneurysms: persistence over time and risk of delayed ischemic events. J. Neurosurg. 2013;118:1014–1022. - PubMed
-
- Mocco J, et al. Treatment of intracranial aneurysms with the Enterprise stent: a multicenter registry. J. Neurosurg. 2009;110:35–39. - PubMed
-
- Campbell BCV, et al. Endovascular stent thrombectomy: the new standard of care for large vessel ischaemic stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14:846–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

