p38 MAPK signaling mediates retinoic acid-induced CD103 expression in human dendritic cells
- PMID: 32737889
- PMCID: PMC7576877
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.13246
p38 MAPK signaling mediates retinoic acid-induced CD103 expression in human dendritic cells
Abstract
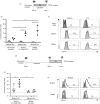
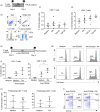
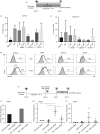
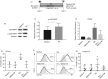
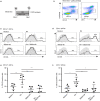
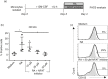
Retinoic acid (RA) is an active derivative of vitamin A and a key regulator of immune cell function. In dendritic cells (DCs), RA drives the expression of CD103 (integrin αE ), a functionally relevant DC subset marker. In this study, we analyzed the cell type specificity and the molecular mechanisms involved in RA-induced CD103 expression. We show that RA treatment caused a significant up-regulation of CD103 in differentiated monocyte-derived DCs and blood DCs, but not in differentiated monocyte-derived macrophages or T cells. DC treatment with an RA receptor α (RARα) agonist led to an increase in CD103 expression similar to that in RA treatment, whereas RARA gene silencing with small interfering RNA blocked RA-induced up-regulation of CD103, pointing to a major role of RARα in the regulation of CD103 expression. To elucidate RA-induced signaling downstream of RARα, we used Western blot analysis of RA-treated DCs and showed a significant increase of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation. In addition, DCs cultured with RA and a p38 MAPK inhibitor had a significantly reduced expression of CD103 compared with DCs cultured with RA only, indicating that p38 MAPK is involved in CD103 regulation. In summary, these findings suggest that the RA-induced expression of CD103 is specific to DCs, is mediated primarily through RARα and involves p38 MAPK signaling.
Keywords: CD103; dendritic cells; p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; retinoic acid.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Vermot J, Gallego Llamas J, Fraulob V, Niederreither K, Chambon P, Dolle P. Retinoic acid controls the bilateral symmetry of somite formation in the mouse embryo. Science 2005; 308:563–6. - PubMed
-
- Erkelens MN, Mebius RE. Retinoic acid and immune homeostasis: a balancing act. Trends Immunol 2017; 38:168–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

