C-Mannosylation Enhances the Structural Stability of Human RNase 2
- PMID: 32739833
- PMCID: PMC7399192
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101371
C-Mannosylation Enhances the Structural Stability of Human RNase 2
Abstract
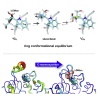
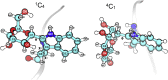
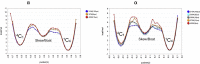
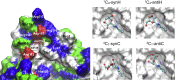
C-Mannosylation is a relatively rare form of protein glycosylation involving the attachment of an α-mannopyranosyl residue to C-2 of the indole moiety of the amino acid tryptophan. This type of linkage was initially discovered in RNase 2 from human urine but later confirmed to be present in many other important proteins. Based on NMR experiments and extensive molecular dynamics simulations on the hundred microsecond timescale we demonstrate that, for isolated glycopeptides and denatured RNase 2, the C-linked mannopyranosyl residue exists as an ensemble of conformations, among which 1C4 is the most abundant. However, for native RNase 2, molecular dynamics and NMR studies revealed that the mannopyranosyl residue favors a specific conformation, which optimally stabilizes the protein fold through a network of hydrogen bonds and which leads to a significant reduction of the protein dynamics on the microsecond timescale. Our findings contribute to the understanding of the biological role of C-mannosylation.
Keywords: Biochemistry; Protein Structure Aspects; Structural Biology.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Agirre J., Davies G.J., Wilson K.S., Cowtan K.D. Carbohydrate structure: the rocky road to automation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017;44:39–47. - PubMed
-
- De Beer T., Vliegenthart J.F., Löffler A., Hofsteenge J. The hexopyranosyl residue that is C-glycosidically linked to the side chain of tryptophan-7 in human RNase Us is alpha-mannopyranose. Biochemistry. 1995;34:11785–11789. - PubMed
-
- Buettner F.F., Ashikov A., Tiemann B., Lehle L., Bakker H. C. elegans DPY-19 is a C-mannosyltransferase glycosylating thrombospondin repeats. Mol. Cell. 2013;50:295–302. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

