Discovery of a Role for Rab3b in Habituation and Cocaine Induced Locomotor Activation in Mice Using Heterogeneous Functional Genomic Analysis
- PMID: 32742255
- PMCID: PMC7364128
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00721
Discovery of a Role for Rab3b in Habituation and Cocaine Induced Locomotor Activation in Mice Using Heterogeneous Functional Genomic Analysis
Abstract
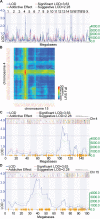
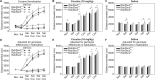
Substance use disorders are prevalent and present a tremendous societal cost but the mechanisms underlying addiction behavior are poorly understood and few biological treatments exist. One strategy to identify novel molecular mechanisms of addiction is through functional genomic experimentation. However, results from individual experiments are often noisy. To address this problem, the convergent analysis of multiple genomic experiments can discern signal from these studies. In the present study, we examine genetic loci that modulate the locomotor response to cocaine identified in the recombinant inbred (BXD RI) genetic reference population. We then applied the GeneWeaver software system for heterogeneous functional genomic analysis to integrate and aggregate multiple studies of addiction genomics, resulting in the identification of Rab3b as a functional correlate of the locomotor response to cocaine in rodents. This gene encodes a member of the RAB family of Ras-like GTPases known to be involved in trafficking of secretory and endocytic vesicles in eukaryotic cells. The convergent evidence for a role of Rab3b includes co-occurrence in previously published genetic mapping studies of cocaine related behaviors; methamphetamine response and cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript prepropeptide (Cartpt) transcript abundance; evidence related to other addictive substances; density of polymorphisms; and its expression pattern in reward pathways. To evaluate this finding, we examined the effect of RAB3 complex perturbation in cocaine response. B6;129-Rab3btm1Sud Rab3ctm1sud Rab3dtm1sud triple null mice (Rab3bcd -/-) exhibited significant deficits in habituation, and increased acute and repeated cocaine responses. This previously unidentified mechanism of the behavioral predisposition and response to cocaine is an example of many that can be identified and validated using aggregate genomic studies.
Keywords: QTL; cocaine sensitization; genetic; genomics; habituation.
Copyright © 2020 Bubier, Philip, Dickson, Mittleman and Chesler.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of genetically complex Collaborative Cross mouse strains that model divergent locomotor activating and reinforcing properties of cocaine.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020 Apr;237(4):979-996. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05429-3. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020. PMID: 31897574 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of genes mediating acute and sensitized locomotor responses to cocaine in BXD/Ty recombinant inbred mice.J Neurosci. 1998 Apr 15;18(8):3023-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-08-03023.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9526019 Free PMC article.
-
The collaborative cross strains and their founders vary widely in cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Oct 5;16:886524. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.886524. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36275853 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabidiol Treatment Might Promote Resilience to Cocaine and Methamphetamine Use Disorders: A Review of Possible Mechanisms.Molecules. 2019 Jul 16;24(14):2583. doi: 10.3390/molecules24142583. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31315244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rab3 proteins and cancer: Exit strategies.J Cell Biochem. 2021 Oct;122(10):1295-1301. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29948. Epub 2021 May 13. J Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33982832 Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding cocaine-induced proteomic adaptations in the mouse nucleus accumbens.Sci Signal. 2024 Apr 16;17(832):eadl4738. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.adl4738. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Sci Signal. 2024. PMID: 38626009 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous fentanyl self-administration in male and female C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 16;13(1):799. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27992-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36646781 Free PMC article.
-
BXD Recombinant Inbred Mice as a Model to Study Neurotoxicity.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 25;11(12):1762. doi: 10.3390/biom11121762. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of isolation housing stress and mouse strain on intravenous cocaine self-administration, sensory stimulus self-administration, and reward preference.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 16;13(1):2810. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29579-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36797314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradberry C. W. (2008). Comparison of acute and chronic neurochemical effects of cocaine and cocaine cues in rhesus monkeys and rodents: focus on striatal and cortical dopamine systems. Rev. Neurosci. 19 113–128. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

