Antibiotics for cancer treatment: A double-edged sword
- PMID: 32742461
- PMCID: PMC7378927
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.47470
Antibiotics for cancer treatment: A double-edged sword
Abstract
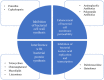
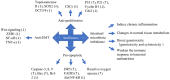
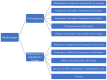
Various antibiotics have been used in the treatment of cancers, via their anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic and anti-epithelial-mesenchymal-transition (EMT) capabilities. However, increasingly studies have indicated that antibiotics may also induce cancer generation by disrupting intestinal microbiota, which further promotes chronic inflammation, alters normal tissue metabolism, leads to genotoxicity and weakens the immune response to bacterial malnutrition, thereby adversely impacting cancer treatment. Despite the advent of high-throughput sequencing technology in recent years, the potential adverse effects of antibiotics on cancer treatments via causing microbial imbalance has been largely ignored. In this review, we discuss the double-edged sword of antibiotics in the field of cancer treatments, explore their potential mechanisms and provide solutions to reduce the potential negative effects of antibiotics.
Keywords: Antibiotics; Cancer; Cancer therapy; Intestinal microbiota disorder.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Kanady K E SWU, Zietman A L, Treatment strategies using transurethral surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy with selection that safely allows bladder conservation for invasive bladder cancer[J] 2015;13(5):359-64. - PubMed
-
- Lordick F HU. Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy[J] Medical Radiology. 2014.
-
- Barrios-González J, Mejýa A. Production of Antibiotics and other Commercially Valuable Secondary Metabolites: Springer New York; 2008.
-
- Xia D. et al. Over-expression of CHAF1A in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer can promote cell proliferation and inhibit cell apoptosis[J] Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications. 2017;486(1):191–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

