A Japanese man with spina bifida who successfully fathered a child following fertility treatment
- PMID: 32743479
- PMCID: PMC7292060
- DOI: 10.1002/iju5.12149
A Japanese man with spina bifida who successfully fathered a child following fertility treatment
Abstract
Introduction: Spina bifida is a congenital anomaly caused by a neural tube closure defect that may result in sexual dysfunction. Sexual dysfunction and infertility are prevalent in spina bifida patients but have been scarcely reported.
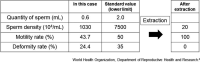
Case presentation: We report the case of a 36-year-old man with spina bifida and mild-moderate erectile dysfunction. He could experience erection and ejaculation. He got married at the age of 28 years, but his wife was unable to conceive for 2 years thereafter. Semen analyses revealed that semen volume, sperm density, and sperm motility rate were below normal levels. It was concluded that natural conception would be difficult, and assisted reproductive strategies were planned. After 4 years, his wife conceived through intracytoplasmic sperm injection and gave birth to a healthy baby.
Conclusion: Fertility treatment, including intracytoplasmic sperm injection, is a useful therapeutic method for male patients with spina bifida who desire to father a child.
Keywords: assisted reproductive technology; conception; fertility treatment; intracytoplasmic sperm injection; spina bifida.
© 2020 The Authors. IJU Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of the Japanese Urological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lapides J, Diokno AC, Silber SJ, Lowe BS. Clean, intermittent self‐catheterization in the treatment of urinary tract disease. J. Urol. 1972; 107: 458–61. - PubMed
-
- Obara K, Mizusawa T, Isahaya E, Suzuki K, Hara N, Takahashi K. Efficacy of clean intermittent catheterization for urinary incontinence in children with neurogenic bladder dysfunction secondary to myelodysplasia. Low. Urin. Tract Symptoms 2010; 2: 100–5. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, Department of Reproductive Health and Research . WHO laboratory manual for the examination of human semen, 5th edn (Internet). 2010. [Cited 30 Jun 2019.]. Available from URL: http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/infertility/978924154...
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources