p16/ki67 and E6/E7 mRNA Accuracy and Prognostic Value in Triaging HPV DNA-Positive Women
- PMID: 32745170
- PMCID: PMC7936054
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djaa105
p16/ki67 and E6/E7 mRNA Accuracy and Prognostic Value in Triaging HPV DNA-Positive Women
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: p16/ki67 and E6/E7 mRNA Accuracy and Prognostic Value in Triaging HPV DNA-Positive Women.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022 Feb 7;114(2):324. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djab107. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022. PMID: 34272943 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
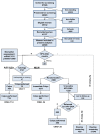
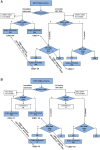
Background: The study presents cross-sectional accuracy of E6 and E7 (E6/E7) mRNA detection and p16/ki67 dual staining, alone or in combination with cytology and human papillomavirus (HPV)16/18 genotyping, as a triage test in HPV DNA-positive women and their impact on cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN2+) overdiagnosis.
Methods: Women aged 25-64 years were recruited. HPV DNA-positive women were triaged with cytology and tested for E6/E7 mRNA and p16/ki67. Cytology positive women were referred to colposcopy, and negatives were randomly assigned to immediate colposcopy or to 1-year HPV retesting. Lesions found within 24 months since recruitment were included. All P values were 2-sided.
Results: 40 509 women were recruited, and 3147 (7.8%) tested HPV DNA positive; 174 CIN2+ were found: sensitivity was 61.0% (95% confidence interval [CI] = 53.6 to 68.0), 94.4% (95% CI = 89.1 to 97.3), and 75.2% (95% CI = 68.1 to 81.6) for cytology, E6/E7 mRNA, and p16/ki67, respectively. Immediate referral was 25.6%, 66.8%, and 28.3%, respectively. Overall referral was 65.3%, 78.3%, and 63.3%, respectively. Cytology or p16/ki67, when combined with HPV16/18 typing, reached higher sensitivity with a small impact on referral. Among the 2306 HPV DNA-positive and cytology-negative women, relative CIN2+ detection in those randomly assigned at 1-year retesting vs immediate colposcopy suggests a -28% CIN2+ regression (95% CI = -57% to +20%); regression was higher in E6/E7 mRNA-negatives (Pinteraction = .29). HPV clearance at 1 year in E6/E7 mRNA and in p16/ki67 negative women was about 2 times higher than in positive women (Pinteraction < .001 for both).
Conclusions: p16/ki67 showed good performance as a triage test. E6/E7 mRNA showed the highest sensitivity, at the price of too high a positivity rate to be efficient for triage. However, when negative, it showed a good prognostic value for clearance and CIN2+ regression.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
The Orderly Incorporation of Continuing Technologic Advances Into Cervical Cancer Screening.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021 Mar 1;113(3):231-233. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djaa106. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021. PMID: 32745173 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ronco G, Meijer CJL, Segnan N, et al.Invasive cervical cancer after HPV-based screening. Lancet. 2014;383(9925):1295. - PubMed
-
- Bosch FX, Robles C, Díaz M, et al.HPV-FASTER: broadening the scope for prevention of HPV-related cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016;13(2):119–132. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. WHO guidelines for screening and treatment of precancerous lesions for cervical cancer prevention. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. https://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/cancers/screening_an.... Accessed June 27, 2019. - PubMed
-
- Ronco G, Arbyn M, Meijer CJLM, et al.Screening for cervical cancer with primary testing for human papillomavirus. In: Anttila A, Arbyn A, De Vuyst H, Dillner J, Dillner L, Franceschi S, Patnick J, Ronco G, Segnan N, Suonio E, Törnberg S, von Karsa L, eds. European Guidelines for Quality Assurance in Cervical Cancer Screening. 2nd ed. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Union; 2015:1–68.
-
- Curry SJ, Krist AH, Owens DK, et al.Screening for cervical cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2018;320(7):674–686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

