Critical COVID-19 disease, homeostasis, and the "surprise" of effective glucocorticoid therapy
- PMID: 32745524
- PMCID: PMC7832484
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108550
Critical COVID-19 disease, homeostasis, and the "surprise" of effective glucocorticoid therapy
Figures
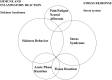
References
-
- Zhang W., Zhao Y., Zhang F., Wang Q., Li T., Liu Z., Wang J., Qin Y., Zhang X., Yan X., Zeng X., Zhang S. The use of anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of people with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): the perspectives of clinical immunologists from China. Clin. Immunol. 2020 May;214 doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108393. (Epub 2020 Mar 25. PMID: 32222466; PMCID: PMC7102614) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chrousos G.P., Trevor A.J. Chapter 39. Adrenocorticosteroids and adrenocortical antagonists. In: Katzung B., Masters S.B., editors. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. 13th edition. Lange, McGraw-Hill; New York, New York: 2015. pp. 680–695.
-
- Meduri G.U., Chrousos G.P. General adaptation in critical illness: glucocorticoid receptor-alpha, master regulator of homeostatic corrections. Front. Endocrinol. 2020;11(1 April) www.frontiersin.org Article 161. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

