Delays and disparities in diagnosis for adults with epilepsy: Findings from U.S. Medicaid data
- PMID: 32745887
- PMCID: PMC7998893
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2020.106406
Delays and disparities in diagnosis for adults with epilepsy: Findings from U.S. Medicaid data
Abstract
Objective: To identify disparities in care pathways and time from first seizure to epilepsy diagnosis, we examined 2010-2014 Medicaid claims (including pharmacy) data from 16 States for individuals with incident epilepsy.
Methods: We identified adults (18-64) with an incident epilepsy diagnosis from 1/2012 through 6/2014. These individuals were enrolled in Medicaid for the entire study period and had no history of anti-epileptic drug (AED) use before their first seizure claim. We identified care pathways and calculated the duration from initial seizure to epilepsy diagnosis. We tested associations between these pathways and race/ethnicity, as well as time differences between care pathways using a Chi-squared and Kruskal-Wallis tests.
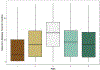
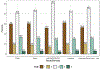
Results: The 14,337 adults followed five different care pathways. Their overall median duration from first seizure code to epilepsy diagnosis code was 19.0 months (interquartile range: 4.6, 30.4), and 56.0% filled an AED prescription. Some minorities were more likely to follow pathways with increased durations and delay to diagnosis, and the duration to diagnosis varied significantly across the care pathways.
Significance: The many different care pathways seen in people with epilepsy show substantial and significant time delays between first seizure diagnosis and epilepsy diagnosis, including significant racial/ethnic disparities that warrant attention.
Keywords: Anti-epileptic drug; Diagnosis; Diagnosis delay; Disparities; Medicaid; Time to diagnosis.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

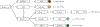

References
-
- Huff JS, Morris DL, Kothari RU, Gibbs MA. Emergency Department Management of Patients with Seizures: A Multicenter Study. Academic Emergency Medicine 2001;8:622–628. - PubMed
-
- Hauser WA, Beghi E. First seizure definitions and worldwide incidence and mortality. Epilepsia 2008;49 Suppl 1:8–12. - PubMed
-
- Berg AT. Risk of recurrence after a first unprovoked seizure. Epilepsia 2008;49 Suppl 1:13–18. - PubMed

