Long-read-based human genomic structural variation detection with cuteSV
- PMID: 32746918
- PMCID: PMC7477834
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-020-02107-y
Long-read-based human genomic structural variation detection with cuteSV
Abstract
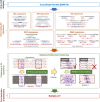
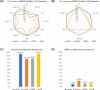
Long-read sequencing is promising for the comprehensive discovery of structural variations (SVs). However, it is still non-trivial to achieve high yields and performance simultaneously due to the complex SV signatures implied by noisy long reads. We propose cuteSV, a sensitive, fast, and scalable long-read-based SV detection approach. cuteSV uses tailored methods to collect the signatures of various types of SVs and employs a clustering-and-refinement method to implement sensitive SV detection. Benchmarks on simulated and real long-read sequencing datasets demonstrate that cuteSV has higher yields and scaling performance than state-of-the-art tools. cuteSV is available at https://github.com/tjiangHIT/cuteSV .
Keywords: Long-read sequencing; Scaling performance; Structural variants detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Rovelet-Lecrux A, Hannequin D, Raux G, Le Meur N, Laquerriere A, Vital A, Dumanchin C, Feuillette S, Brice A, Vercelletto M, et al. APP locus duplication causes autosomal dominant early-onset Alzheimer disease with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Nat Genet. 2006;38:24–26. doi: 10.1038/ng1718. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

