Necroptosis-based CRISPR knockout screen reveals Neuropilin-1 as a critical host factor for early stages of murine cytomegalovirus infection
- PMID: 32747526
- PMCID: PMC7443917
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1921315117
Necroptosis-based CRISPR knockout screen reveals Neuropilin-1 as a critical host factor for early stages of murine cytomegalovirus infection
Abstract
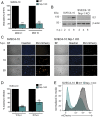
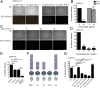
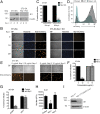
Herpesviruses are ubiquitous human pathogens that cause a wide range of health complications. Currently, there is an incomplete understanding of cellular factors that contribute to herpesvirus infection. Here, we report an antiviral necroptosis-based genetic screen to identify novel host cell factors required for infection with the β-herpesvirus murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV). Our genome-wide CRISPR-based screen harnessed the capacity of herpesvirus mutants that trigger antiviral necroptotic cell death upon early viral gene expression. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and semaphorin-binding receptor Neuropilin-1 (Nrp-1) emerge as crucial determinants of MCMV infection. We find that elimination of Nrp-1 impairs early viral gene expression and reduces infection rates in endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages. Furthermore, preincubation of virus with soluble Nrp-1 dramatically inhibits infection by reducing virus attachment. Thus, Nrp-1 is a key determinant of the initial phase of MCMV infection.
Keywords: CRISPR; cytomegolovirus; necroptosis; neuropilin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Barber G. N., Host defense, viruses and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 8, 113–126 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

