Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19
- PMID: 32747721
- PMCID: PMC7396720
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-020-0485-4
Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19
Abstract
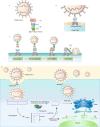
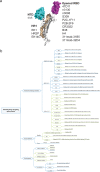
Coronavirus disease 2019 is a newly emerging infectious disease currently spreading across the world. It is caused by a novel coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV-2, which plays a key role in the receptor recognition and cell membrane fusion process, is composed of two subunits, S1 and S2. The S1 subunit contains a receptor-binding domain that recognizes and binds to the host receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, while the S2 subunit mediates viral cell membrane fusion by forming a six-helical bundle via the two-heptad repeat domain. In this review, we highlight recent research advance in the structure, function and development of antivirus drugs targeting the S protein.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 virus; antibodies; antivirus drugs; fusion inhibitors; host proteases inhibitors; spike protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
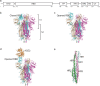
References
-
- Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB. Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA. 2020;323:1824–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

