Bidirectional Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdowns on Health Behaviors and Quality of Life among Chinese Adults
- PMID: 32748825
- PMCID: PMC7432516
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17155575
Bidirectional Influence of the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdowns on Health Behaviors and Quality of Life among Chinese Adults
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has created challenges that have caused profound changes in health behaviors. This study aimed to explore how COVID-19 is affecting the health-related quality of life (QoL) among Chinese adults.
Methods: The data of health-related behaviors and QoL were collected via online surveys from 2289 adults (mean age = 27.8 ± 12 years) who had been isolated at home for an average of 77 days.
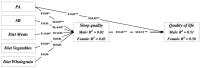
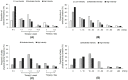
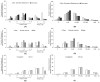
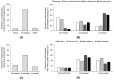
Results: More than 50% of the respondents reported that their time engaged in daily physical activity (PA) decreased, while sedentary behavior (SB) time increased compared with that before the lockdown. Only 20% of the respondents reported engaging in moderate-to-vigorous PA, 23% of adults reported changed their diets to be healthier, and 30% reported consuming more vegetables, fruits, and milk products than before home-isolation. During home-isolation, 75.2% of the adults rated their sleep quality as very good, and 65% reported that they were satisfied with their QoL. Sleep quality mediated the relationship between PA and QoL.
Conclusion: The two-to-three-month home-isolation has had mixed effects on adult health behaviors in China. The participants were found to have focused more on their eating quality and patterns, which had a positive influence on their QoL. However, people should be encouraged to exercise at home with limited space to maintain a generally healthy lifestyle during a prolonged quarantine.
Keywords: diet; pandemic; physical activity; sedentary behavior; sleep.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Johns Hopkins University Coronavirus COVID-19 Global Cases by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University. [(accessed on 21 June 2020)]; Available online: https://www.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594740fd4029 94....
-
- World Health Organization Statement on the Second Meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee Regarding the outbreak of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) [(accessed on 30 January 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-...
-
- Shanghai Municipal People’s Government Shanghai Municipal People’s Government on the Further Strict Implementation of the Epidemic Prevention and Control Measures Circular. [(accessed on 10 February 2020)]; Available online: http://www.shanghai.gov.cn/nw2/nw2314/nw2319/nw123 44/u26aw63661.html.
-
- CBN weekly, Omron Health Urban Stress Survey Report Shanghai. [(accessed on 10 June 2018)]; Available online: http://www.cnr.cn/shanghai/tt/20180610/t20180610_524264808.shtml.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

