Smartphone App with an Accelerometer Enhances Patients' Physical Activity Following Elective Orthopedic Surgery: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 32748876
- PMCID: PMC7436024
- DOI: 10.3390/s20154317
Smartphone App with an Accelerometer Enhances Patients' Physical Activity Following Elective Orthopedic Surgery: A Pilot Study
Abstract
Low physical activity (PA) levels are common in hospitalized patients. Digital health tools could be valuable in preventing the negative effects of inactivity. We therefore developed Hospital Fit; which is a smartphone application with an accelerometer, designed for hospitalized patients. It enables objective activity monitoring and provides patients with insights into their recovery progress and offers a tailored exercise program. The aim of this study was to investigate the potential of Hospital Fit to enhance PA levels and functional recovery following orthopedic surgery. PA was measured with an accelerometer postoperatively until discharge. The control group received standard physiotherapy, while the intervention group used Hospital Fit in addition to physiotherapy. The time spent active and functional recovery (modified Iowa Level of Assistance Scale) on postoperative day one (POD1) were measured. Ninety-seven patients undergoing total knee or hip arthroplasty were recruited. Hospital Fit use, corrected for age, resulted in patients standing and walking on POD1 for an average increase of 28.43 min (95% confidence interval (CI): 5.55-51.32). The odds of achieving functional recovery on POD1, corrected for the American Society of Anesthesiologists classification, were 3.08 times higher (95% CI: 1.14-8.31) with Hospital Fit use. A smartphone app combined with an accelerometer demonstrates the potential to enhance patients' PA levels and functional recovery during hospitalization.
Keywords: activity monitoring; arthroplasty; functional recovery; hospitalization; mHealth; physical activity; physiotherapy; wearable sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. All subjects gave their informed consent for inclusion before study initiation. This study was performed in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki and the protocol was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the University Hospital Maastricht and Maastricht University (METC azM/UM), registration number 2017-0175.
Figures
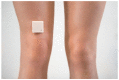



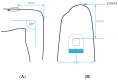

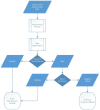
References
-
- AJRR . 2019 Annual Report. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS); Rosemont, IL, USA: 2019.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

