The effect of smoking on COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32749705
- PMCID: PMC7436545
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.26389
The effect of smoking on COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
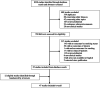
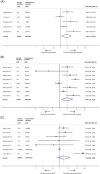
Various comorbidities represent risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The impact of smoking on COVID-19 severity has been previously reported in several meta-analyses limited by small sample sizes and poor methodology. We aimed to rigorously and definitively quantify the effects of smoking on COVID-19 severity. MEDLINE, Embase, CENTRAL, and Web of Science were searched between 1 December 2019 and 2 June 2020. Studies reporting smoking status of hospitalized patients with different severities of disease and/or at least one clinical endpoint of interest (disease progression, intensive care unit admission, need for mechanical ventilation, and mortality) were included. Data were pooled using a random-effects model. This study was registered on PROSPERO: CRD42020180920. We analyzed 47 eligible studies reporting on 32 849 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, with 8417 (25.6%) reporting a smoking history, comprising 1501 current smokers, 5676 former smokers, and 1240 unspecified smokers. Current smokers had an increased risk of severe COVID-19 (risk ratios [RR]: 1.80; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.14-2.85; P = .012), and severe or critical COVID-19 (RR: 1.98; CI: 1.16-3.38; P = .012). Patients with a smoking history had a significantly increased risk of severe COVID-19 (RR: 1.31; CI: 1.12-1.54; P = .001), severe or critical COVID-19 (RR: 1.35; CI: 1.19-1.53; P < .0001), in-hospital mortality (RR: 1.26; CI: 1.20-1.32; P < .0001), disease progression (RR: 2.18; CI: 1.06-4.49; P = .035), and need for mechanical ventilation (RR: 1.20; CI: 1.01-1.42; P = .043). Patients with any smoking history are vulnerable to severe COVID-19 and worse in-hospital outcomes. In the absence of current targeted therapies, preventative, and supportive strategies to reduce morbidity and mortality in current and former smokers are crucial.
Keywords: coronavirus; epidemiology; pandemics; pathogenesis; respiratory tract; virus classification; zoonoses.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Medical Virology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- WHO . Coronavirus disease (COVID‐19) Situation Report ‐ 190. July 28 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... Accessed July 29, 2020.
-
- Johns Hopkins University and Medicine Coronavirus Resource Center . COVID‐19 World Map. July 29 2020. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html. Accessed July 29, 2020.
-
- Wu Z, McCoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention [published online ahead of print February 24, 2020]. JAMA. 10.1001/jama.2020.2648 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

