IsoSearch: An Untargeted and Unbiased Metabolite and Lipid Isotopomer Tracing Strategy from HR-LC-MS/MS Datasets
- PMID: 32751454
- PMCID: PMC7563207
- DOI: 10.3390/mps3030054
IsoSearch: An Untargeted and Unbiased Metabolite and Lipid Isotopomer Tracing Strategy from HR-LC-MS/MS Datasets
Abstract
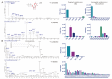
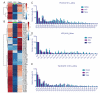
Stable isotopic tracer analysis is a technique used to determine carbon or nitrogen atom incorporation into biological systems. A number of mass spectrometry based approaches have been developed for this purpose, including high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry (HR-LC-MS/MS), selected reaction monitoring (SRM) and parallel reaction monitoring (PRM). We have developed an approach for analyzing untargeted metabolomic and lipidomic datasets using high-resolution mass spectrometry with polarity switching and implemented our approach in the open-source R script IsoSearch and in Scaffold Elements software. Using our strategy, which requires an unlabeled reference dataset and isotope labeled datasets across various biological conditions, we traced metabolic isotopomer alterations in breast cancer cells (MCF-7) treated with the metabolic drugs 2-deoxy-glucose, 6-aminonicotinamide, compound 968, and rapamycin. Metabolites and lipids were first identified by the commercial software Scaffold Elements and LipidSearch, then IsoSearch successfully profiled the 13C-isotopomers extracted metabolites and lipids from 13C-glucose labeled MCF-7 cells. The results interpreted known models, such as glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathway inhibition, but also helped to discover new metabolic/lipid flux patterns, including a reactive oxygen species (ROS) defense mechanism induced by 6AN and triglyceride accumulation in rapamycin treated cells. The results suggest the IsoSearch/Scaffold Elements platform is effective for studying metabolic tracer analysis in diseases, drug metabolism, and metabolic engineering for both polar metabolites and non-polar lipids.
Keywords: 13C; 15N; LC-MS/MS; cancer; cell culture; flux; glucose; glutamine; high resolution; isotopic tracer analysis; lipidomics; liquid chromatography; mass spectrometry; metabolism; metabolomics; polarity switching; stable isotope labeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Buescher J.M., Antoniewicz M.R., Boros L.G., Burgess S.C., Brunengraber H., Clish C.B., DeBerardinis R.J., Feron O., Frezza C., Ghesquiere B., et al. A roadmap for interpreting (13)C metabolite labeling patterns from cells. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015;34:189–201. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2015.02.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sriram G., Fulton D.B., Iyer V.V., Peterson J.M., Zhou R., Westgate M.E., Spalding M.H., Shanks J.V. Quantification of compartmented metabolic fluxes in developing soybean embryos by employing biosynthetically directed fractional (13)C labeling, two-dimensional [(13)C, (1)H] nuclear magnetic resonance, and comprehensive isotopomer balancing. Plant. Physiol. 2004;136:3043–3057. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.050625. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hellerstein M.K., Murphy E. Stable isotope-mass spectrometric measurements of molecular fluxes in vivo: Emerging applications in drug development. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2004;6:249–264. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

