Short-Term Compound Training on Physical Performance in Young Soccer Players
- PMID: 32751640
- PMCID: PMC7466703
- DOI: 10.3390/sports8080108
Short-Term Compound Training on Physical Performance in Young Soccer Players
Abstract
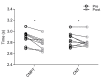
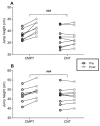
This study aimed to investigate the effects of a five-week compound training (with strength and plyometric exercises performed on separate days) on sprint, change of direction, and vertical jump in young soccer players. Eighteen novices in strength and plyometric training were assigned to either a compound training (CMPT) or a control condition (CNT). Both groups trained three times per week. One session was dedicated to soccer-specific drills. The other two weekly sessions were dedicated to circuit-based training routines employing on one-day strength exercises and on the other day plyometric exercises in the CMPT group. At the same time, the CNT group performed two weekly soccer-specific training sessions. All players were tested by 15-m sprint, change-of-direction and acceleration test (CODAT), squat jump, and countermovement jump with arms swing tests. CMPT group improved CODAT, squat jump and countermovement jump to a higher extent compared to CNT group (large vs small or trivial effects, p < 0.05), while both groups had similar 15-m sprint performance (p > 0.05). These results support the use of compound training to improve change of direction and vertical jump performances in young novice soccer players, which are unfamiliar with structured and advanced strength and plyometric training.
Keywords: plyometrics; strength training; team sport; testing; youth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Plyometric and Directional Training on Physical Fitness Parameters in Youth Soccer Players.Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2019 Mar 1;14(3):392-398. doi: 10.1123/ijspp.2018-0545. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2019. PMID: 30204520 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness and time-course adaptation of resistance training vs. plyometric training in prepubertal soccer players.J Sport Health Sci. 2020 Dec;9(6):620-627. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2016.07.008. Epub 2016 Jul 16. J Sport Health Sci. 2020. PMID: 33308812 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of vertical and horizontal plyometric training on jump performances and sprint force-velocity profile in young elite soccer players.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024 Sep;124(9):2591-2601. doi: 10.1007/s00421-024-05477-4. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38602544
-
Effects of Plyometric Training with Agility Ladder on Physical Fitness in Youth Soccer Players.Int J Sports Med. 2021 Sep;42(10):896-904. doi: 10.1055/a-1308-3316. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Int J Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 33592641 Clinical Trial.
-
Programming Plyometric-Jump Training in Soccer: A Review.Sports (Basel). 2022 Jun 10;10(6):94. doi: 10.3390/sports10060094. Sports (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736834 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Observational Screening Guidelines and Smartphone Accelerometer Thresholds to Establish the Intensity of Some of the Most Popular Core Stability Exercises.Front Physiol. 2021 Oct 22;12:751569. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.751569. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34744790 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of speed, agility and quickness training programme on cognitive and physical performance in preadolescent soccer players.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 1;17(12):e0277683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277683. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36454889 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
High-Load Strength Training Reduces Injury Incidence and Injury Burden and Improves Physical Fitness in Young Highly Trained Soccer Players.Sports Health. 2025 Apr 27:19417381251333417. doi: 10.1177/19417381251333417. Online ahead of print. Sports Health. 2025. PMID: 40289456 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Fitness and Upper Limb Asymmetry in Young Padel Players: Differences between Genders and Categories.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 26;19(11):6461. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19116461. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35682046 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Non-Sport-Specific Versus Sport-Specific Training on Physical Performance and Perceptual Response in Young Football Players.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Feb 18;18(4):1962. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18041962. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33670481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Radzimiński Ł., Hajduczenia A. Influence of different forms of creatine supplementation on aerobic and anaerobic capacity of soccer players during preparation period. Atena J. Sports Sci. 2019;1:18.
-
- Lloyd R.S., Meyers R.W., Oliver J.L. The Natural Development and Trainability of Plyometric Ability during Childhood. Strength Cond. J. 2011;33:23–32. doi: 10.1519/SSC.0b013e3182093a27. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

