MicroRNA-Dependent Targeting of RSU1 and the IPP Adhesion Complex Regulates the PTEN/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 32751711
- PMCID: PMC7432699
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21155458
MicroRNA-Dependent Targeting of RSU1 and the IPP Adhesion Complex Regulates the PTEN/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
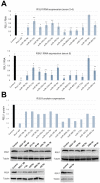
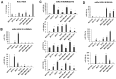
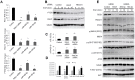
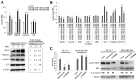
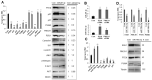
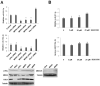
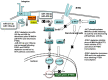
(1) Background: The microRNA (miR)-directed control of gene expression is correlated with numerous physiological processes as well as the pathological features of tumors. The focus of this study is on the role of miRs in the regulation of RSU1 and proteins in the IPP (integrin linked kinase, PINCH and parvin) complex. Because the IPP adaptor proteins link β integrins to actin cytoskeleton, and the RSU1 signaling protein connects the complex to the activation of cJun, ATF2 and the transcription of PTEN, their reduction by miRs has the potential to alter both adhesion and survival signaling. (2) Methods: Multiple database analyses were used to identify miRs that target RSU1 and PINCH1. miR transfection validated the effects of miRs on RSU1, PINCH1 and downstream targets in breast cancer cell lines. (3) Results: The miRs targeting RSU1 mRNA include miR-182-5p, -409-3p, -130a-3p, -221-3p, -744-5p and -106b-5p. Data show that miR-182-5p and -409-3p reduce RSU1, PINCH1 and inhibit the ATF2 activation of PTEN expression. miR-221-3p and miR-130a-3p target RSU1 and PINCH1 and, conversely, RSU1 depletion increases miR-221-3p and miR-130a-3p. (4) Conclusions: miRs targeting RSU1 and PINCH1 in mammary epithelial or luminal breast cancer cell lines reduced RSU1 signaling to p38 MAP kinase and ATF2, inhibiting the expression of PTEN. miR-221-3p, known to target PTEN and cell cycle regulators, also targets RSU1 and PINCH1 in luminal breast cancer cell lines.
Keywords: LIMS1; PINCH1; PTEN; RSU1; micro RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. Disclaimer: The opinions expressed here are those of the authors and should not be construed as official policy or reflecting the views of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences or the Department of the Navy, Army, Department of Defense, nor the U.S. Government.
Figures
References
-
- Rupaimoole R., Calin G.A., Lopez-Berestein G., Sood A.K. miRNA Deregulation in Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2016;6:235–246. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0893. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Horton E.R., Byron A., Askari J.A., Ng D.H.J., Millon-Fremillon A., Robertson J., Koper E.J., Paul N.R., Warwood S., Knight D., et al. Definition of a consensus integrin adhesome and its dynamics during adhesion complex assembly and disassembly. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015;17:1577–1587. doi: 10.1038/ncb3257. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

