Preliminary Study of Sars-Cov-2 Occurrence in Wastewater in the Czech Republic
- PMID: 32751749
- PMCID: PMC7432771
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17155508
Preliminary Study of Sars-Cov-2 Occurrence in Wastewater in the Czech Republic
Abstract
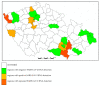
The virus SARS-CoV-2, which has caused the recent COVID-19 pandemic, may be present in the stools of COVID-19 patients. Therefore, we aimed to detect SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater for surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in the population. Samples of untreated wastewater were collected from 33 wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) of different sizes within the Czech Republic. SARS-CoV-2 RNA was concentrated from wastewater and viral RNA was determined using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected in 11.6% of samples and more than 27.3% of WWTPs; in some of them, SARS-CoV-2 was detected repeatedly. Our preliminary results indicate that an epidemiology approach that focuses on the determination of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater could be suitable for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance in the population.
Keywords: RT-qPCR; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; early warning system; epidemic; virus; wastewater; wastewater-based epidemiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ding Y., He L., Zhang Q., Huang Z., Che X., Hou J., Wang H., Shen H., Qiu L., Li Z., et al. Organ distribution of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) in SARS patients: Implications for pathogenesis and virus transmission pathways. J. Pathol. 2004;203:622–630. doi: 10.1002/path.1560. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous