Localization of the Elastic Proteins in the Flight Muscle of Manduca sexta
- PMID: 32752103
- PMCID: PMC7432240
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21155504
Localization of the Elastic Proteins in the Flight Muscle of Manduca sexta
Abstract
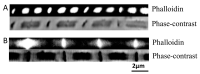
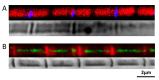
The flight muscle of Manduca sexta (DLM1) is an emerging model system for biophysical studies of muscle contraction. Unlike the well-studied indirect flight muscle of Lethocerus and Drosophila, the DLM1 of Manduca is a synchronous muscle, as are the vertebrate cardiac and skeletal muscles. Very little has been published regarding the ultrastructure and protein composition of this muscle. Previous studies have demonstrated that DLM1 express two projectin isoform, two kettin isoforms, and two large Salimus (Sls) isoforms. Such large Sls isoforms have not been observed in the asynchronous flight muscles of Lethocerus and Drosophila. The spatial localization of these proteins was unknown. Here, immuno-localization was used to show that the N-termini of projectin and Salimus are inserted into the Z-band. Projectin spans across the I-band, and the C-terminus is attached to the thick filament in the A-band. The C-terminus of Sls was also located in the A-band. Using confocal microscopy and experimental force-length curves, thin filament lengths were estimated as ~1.5 µm and thick filament lengths were measured as ~2.5 µm. This structural information may help provide an interpretive framework for future studies using this muscle system.
Keywords: Manduca sexta; elastic proteins; myofilament lengths; sarcomere structures; synchronous insect flight muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Elastic proteins in the flight muscle of Manduca sexta.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Feb 15;568:16-27. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2014.12.033. Epub 2015 Jan 17. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 25602701 Free PMC article.
-
The function of elastic proteins in the oscillatory contraction of insect flight muscle.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2005;26(6-8):479-85. doi: 10.1007/s10974-005-9032-7. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2005. PMID: 16450058 Review.
-
Kettin, a major source of myofibrillar stiffness in Drosophila indirect flight muscle.J Cell Biol. 2001 Sep 3;154(5):1045-57. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200104016. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11535621 Free PMC article.
-
Myofilament proteins in the synchronous flight muscles of Manduca sexta show both similarities and differences to Drosophila melanogaster.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Jul;62:174-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2015.02.008. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25797474
-
Drosophila projectin: a look at protein structure and sarcomeric assembly.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000;481:251-62; discussion 262-4. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4267-4_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000. PMID: 10987077 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of muscle ultrastructure on the force, displacement and work capacity of skeletal muscle.J R Soc Interface. 2024 May;21(214):20230658. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2023.0658. Epub 2024 May 22. J R Soc Interface. 2024. PMID: 38774960 Free PMC article.
-
Long read genome assembly of Automeris io (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae) an emerging model for the evolution of deimatic displays.G3 (Bethesda). 2024 Mar 6;14(3):jkad292. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkad292. G3 (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 38324397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boettiger E.G. The machinery of insect flight. In: Scheer B.T., editor. Recent Adv. Invertebr. Physiol. Univ. of Oregon Publication; Eugene, OR, USA: 1957. pp. 117–142.
-
- Boettiger E.G. Insect flight muscles and their basic physiology. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1960;5:1–16. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.05.010160.000245. - DOI
-
- Josephson R.K., Malamud J.G., Stokes D.R. Asynchronous muscle. J. Exp. Biol. 2000;203:2713–2722. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

