The Pandemic League of COVID-19: Korea Versus the United States, With Lessons for the Entire World
- PMID: 32752591
- PMCID: PMC7411243
- DOI: 10.3961/jpmph.20.166
The Pandemic League of COVID-19: Korea Versus the United States, With Lessons for the Entire World
Abstract
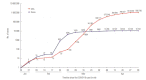
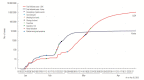
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is inflicting a brutal blow on humankind, and no corner of the world has been exempted from its wrath. This study analyzes the chief control measures and the distinctive features of the responses implemented by Korea and the United States to contain COVID-19 with the goal of extracting lessons that can be applied globally. Even though both nations reported their index cases on the same day, Korea succeeded in flattening the curve, with 10 752 cases as of April 28, 2020, whereas the outbreak skyrocketed in the United States, which had more than 1 million cases at the same time. The prudent and timely execution of control strategies enabled Korea to tame the spread of the virus, whereas the United States paid a major price for its delay, although it is too early to render a conclusive verdict. Information pertaining to the number of people infected with the virus and measures instituted by the government to control the spread of COVID-19 was retrieved from the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention websites and press releases. Drawing lessons from both nations, it is evident that the resolution to the COVID-19 pandemic lies in the prudent usage of available resources, proactive strategic planning, public participation, transparency in information sharing, abiding by the regulations that are put into place, and how well the plan of action is implemented.
Keywords: COVID-19; Containment; Coronavirus; Pandemic; Quarantine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the material presented in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safe hospital preparedness in the era of COVID-19: The Swiss cheese model.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Sep;98:294-296. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.094. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32619759 Free PMC article.
-
A Bold Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic: Medical Students, National Service, and Public Health.JAMA. 2020 May 12;323(18):1790-1791. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6166. JAMA. 2020. PMID: 32267488 No abstract available.
-
Searching for Digital Technologies in Containment and Mitigation Strategies: Experience from South Korea COVID-19.Ann Glob Health. 2020 Aug 31;86(1):109. doi: 10.5334/aogh.2993. Ann Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32944506 Free PMC article.
-
The coronavirus pandemic in Malaysia: A commentary.Psychol Trauma. 2020 Jul;12(5):482-484. doi: 10.1037/tra0000897. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Psychol Trauma. 2020. PMID: 32584114 Review.
-
Efficacy of Mass Quarantine as Leverage of Health System Governance During COVID-19 Outbreak: A Mini Policy Review.Arch Iran Med. 2020 Apr 1;23(4):265-267. doi: 10.34172/aim.2020.08. Arch Iran Med. 2020. PMID: 32271600 Review.
Cited by
-
Government Initiatives for Research Ethics During COVID-19 Pandemic in Korea.J Korean Med Sci. 2024 Apr 1;39(12):e116. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e116. J Korean Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38565174 Free PMC article.
-
Scrutiny of COVID-19 response strategies among severely affected European nations.Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021 Aug;12(4):203-214. doi: 10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0068. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021. PMID: 34465070 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges posed by COVID-19 and neurosurgical nursing strategies in developing countries.Surg Neurol Int. 2020 Dec 16;11:441. doi: 10.25259/SNI_677_2020. eCollection 2020. Surg Neurol Int. 2020. PMID: 33408926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of public health measures in reducing the incidence of covid-19, SARS-CoV-2 transmission, and covid-19 mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ. 2021 Nov 17;375:e068302. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2021-068302. BMJ. 2021. PMID: 34789505 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Knowledge, Preventive Practices, and Depression Among Chinese International Students and Local Korean Students in South Korea During the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Online Cross-Sectional Study.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Jun 21;13:920887. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.920887. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35815006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Worldometer Coronavirus: COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic. [cited 2020 Apr 28]. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/?fbclid=IwAR0RYMPhu-J9i5t74sla....
-
- World Bank Population density (people per sq. km of land area) - Korea, Rep., United States. [cited 2020 Apr 29]. Available from: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EN.POP.DNST? locations=KR-US.
-
- United Nations Development Programme Human development reports: 2019 Human Development Index ranking. [cited 2020 Apr 30]. Available from: http://hdr.undp.org/en/content/2019-human-development-index-ranking.
-
- Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention The updates on COVID-19 in Korea as of 16 April. [cited 2020 May 20]. Available from: https://www.cdc.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a30402000000&bid=0030&act=view&....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous