Tailoring B cell depletion therapy in MS according to memory B cell monitoring
- PMID: 32753406
- PMCID: PMC7413707
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000845
Tailoring B cell depletion therapy in MS according to memory B cell monitoring
Abstract
Objective: We wanted to evaluate efficacy on inflammatory parameters of rituximab (RTX)-personalized reinfusion scheme using a memory B cell-based treatment regimen.
Methods: This is a prospective, uncontrolled, open-label study including patients with MS treated with RTX in 2 Italian MS units. All patients were treated with RTX induction, followed by maintenance infusion at the dosage of 375 mg/m2, according to memory B cell repopulation (0.05% of peripheral-blood mononuclear cells [PBMCs] for the first 2 years, 0.1% of PBMC for the third year). MS activity was assessed as clinical or MRI activity.
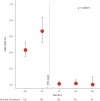
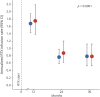
Results: One hundred two patients were included in the analysis. Mean follow-up was 2.40 years (range 0.57-7.15 years). The annualized relapse rate (ARR) was 0.67 in the year before RTX start and decreased to 0.01 in the 3 years after RTX initiation (global ARR). The proportion of patient with MS activity (i.e., relapse or MRI activity) was 63.16% in the year before RTX start and decreased to 8.7% (0-6 months), 1.3% (6-12 months), 0% (12-24 months), and 0% (24-36 months). Annualized RTX infusion rates were 1.67 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.43-1.94), 0.76 (95% CI: 0.58-0.98), and 0.78 (95% CI: 0.52-1.12) for the first 3 years after RTX initiation, respectively. Patients were reinfused with a mean infusion interval of 367 days (range 181-839 days).
Conclusion: The results of this study show that the memory B cell-based RTX reinfusion protocol is able to reduce the mean number of RTX reinfusions with persistent reduction of disease activity.
Classification of evidence: This study provides Class IV evidence that for patients with MS, a memory B cell-based RTX reinfusion protocol can reduce the mean number of RTX reinfusions with persistent reduction of disease activity.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- Hauser SL, Bar-Or A, Comi G, et al. . Ocrelizumab versus interferon beta-1a in relapsing multiple sclerosis. New Engl J Med 2017;376:221–234. - PubMed
-
- Zecca C, Bovis F, Novi G, et al. . Treatment of multiple sclerosis with rituximab: a multicentric Italian–Swiss experience. Mult Scler J 2019. Epub 2019 Oct 1. - PubMed
-
- Berntsson SG, Kristoffersson A, Boström I, Feresiadou A, Burman J, Landtblom AM. Rapidly increasing off-label use of rituximab in multiple sclerosis in Sweden—outlier or predecessor? Acta Neurol Scand 2018;138:327–331. - PubMed
-
- SmPC Ocrelizumab [Internet]. 2019. Available at: ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/ocrevus-epar-product-info.... Accessed May 28, 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
