SARS-CoV-2 RNA Dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) - A drug repurposing study
- PMID: 32754651
- PMCID: PMC7377705
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04502
SARS-CoV-2 RNA Dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) - A drug repurposing study
Abstract
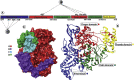
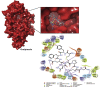
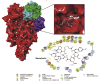
The outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 in December 2019 in China subsequently lead to a pandemic. Lack of vaccine and specific anti-viral drugs started a global health disaster. For a sustained control and protection, development of potential anti-viral drugs is one of the targeted approach. Although, designing and developing a panel of new drugs molecules are always encouraged. However, in the current emergency, drug repurposing study is one of the most effective and fast track option. The crystal structure of a SARS-CoV-2 (Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) RNA Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp) has recently been deciphered through X-ray crystallography. The single-chain of core RNA Dependent RNA Polymerase relies on virus-encoded cofactors nsp7 and two units of nsp8 for its optimum function. This study explored the FDA approved database of 7922 molecules and screened against the core polymerase along with cofactors. Here we report a panel of FDA approved drugs that show substantial interactions with key amino acid residues of the active site. Interestingly, some of the identified drugs (Ornipressin, Lypressin, Examorelin, Polymyxin B1) bind strongly within the binding pockets of both forms of RdRp. Besides, we found strong candidates for the complex form as well which include Nacortocin, Cistinexine, Cisatracurium (among others). These drugs have the potential to be considered while contriving therapeutic options.
Keywords: Biochemistry; Bioinformatics; Biological sciences; COVID-19; Drug repurposing; Molecular biology; Molecular docking simulation; Pharmaceutical science; RNA Dependent RNA polymerase; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

