High Respiratory Drive and Excessive Respiratory Efforts Predict Relapse of Respiratory Failure in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 32755309
- PMCID: PMC7560807
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202005-1582LE
High Respiratory Drive and Excessive Respiratory Efforts Predict Relapse of Respiratory Failure in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19
Figures
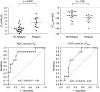
Comment in
-
The Respiratory Drive: An Overlooked Tile of COVID-19 Pathophysiology.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Oct 15;202(8):1079-1080. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202008-3142ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32881583 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Brochard L, Slutsky A, Pesenti A. Mechanical ventilation to minimize progression of lung injury in acute respiratory failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:438–442. - PubMed
-
- Telias I, Damiani F, Brochard L. The airway occlusion pressure (P0.1) to monitor respiratory drive during mechanical ventilation: increasing awareness of a not-so-new problem. Intensive Care Med. 2018;44:1532–1535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

