Blacks Are Less Likely to Present With Strokes During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Observations From the Buckle of the Stroke Belt
- PMID: 32755454
- PMCID: PMC7434003
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.031121
Blacks Are Less Likely to Present With Strokes During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Observations From the Buckle of the Stroke Belt
Abstract
Background and purpose: The impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on stroke systems has not been systematically evaluated. Our study aims to investigate trends in telestroke consults during the pandemic.
Methods: We did retrospective chart review of consecutive patients seen through a telestroke network in South Carolina from March 2019 to April 2020. We dichotomized patients to preCOVID-19 pandemic (March 2019 to February 2020) and during COVID-19 pandemic (March to April 2020).
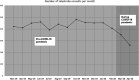
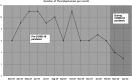
Results: A total of 5852 patients were evaluated during the study period, 613 (10.5%) were seen during the pandemic. The median number of weekly consults dropped from 112 to 77 during the pandemic, P=0.002. There was no difference in baseline features; however, Black patients were less likely to present with strokes during the pandemic (13.9% versus 29%, P≤0.002).
Conclusions: The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a significant drop in telestroke volume. The impact seems to disproportionately affect Black patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; South Carolina; pandemic; stroke; thrombolysis.
Figures
References
-
- Johns Hopkins University. COVID-19 dashboard by the center for systems science and engineering. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html. Accessed May 09, 2020.
-
- Mao L, Jin H, Wang M, Hu Y, Chen S, He Q, Chang J, Hong C, Zhou Y, Wang D, et al. Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020; 77:1–9https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/2764549. Accessed May,08, 2020 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babu Welch MD. Are stroke sufferers silent victims of COVID-19? https://utswmed.Org/medblog/covid19-stroke-volume-decrease/. Accessed May 09, 2020.
-
- Kansagra AP, Goyal MS, Hamilton S, Albers GW. Collateral effect of covid-19 on stroke evaluation in the united states. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:NEJMc2014816.https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2014816. Accessed May 08, 2020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous