ARIMA modelling & forecasting of COVID-19 in top five affected countries
- PMID: 32755845
- PMCID: PMC7386367
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.07.042
ARIMA modelling & forecasting of COVID-19 in top five affected countries
Abstract
Background and aims: In a little over six months, the Corona virus epidemic has affected over ten million and killed over half a million people worldwide as on June 30, 2020. With no vaccine in sight, the spread of the virus is likely to continue unabated. This article aims to analyze the time series data for top five countries affected by the COVID-19 for forecasting the spread of the epidemic.
Material and methods: Daily time series data from 15th February to June 30, 2020 of total infected cases from the top five countries namely US, Brazil, India, Russia and Spain were collected from the online database. ARIMA model specifications were estimated using Hannan and Rissanen algorithm. Out of sample forecast for the next 77 days was computed using the ARIMA models.
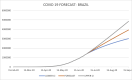
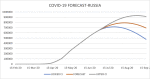
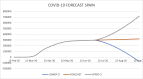
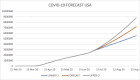
Results: Forecast for the first 18 days of July was compared with the actual data and the forecast accuracy was using MAD and MAPE were found within acceptable agreement. The graphic plots of forecast data suggest that While Russia and Spain have reached the inflexion point in the spread of epidemic, the US, Brazil and India are still experiencing an exponential curve.
Conclusion: Our analysis shows that India and Brazil will hit 1.38 million and 2.47 million mark while the US will reach the 4.29 million mark by 31st July. With no effective cure available at the moment, this forecast will help the governments to be better prepared to combat the epidemic by ramping up their healthcare facilities.
Keywords: ARIMA; COVID-19; Forecasting; Pandemic; SARV-2 Cov.
Copyright © 2020 Diabetes India. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest On behalf of my co-authors, I, Dr. Alok Kumar Sahai, confirm that none of the authors have any conflict of interest to report.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comments on "ARIMA modelling & forecasting of COVID-19 in top five affected countries"(by Sahai et al.).Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020 Nov-Dec;14(6):1989-1990. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.10.006. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020. PMID: 33080540 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Coronavirus Update (Live) Cases and 501644 deaths from COVID-19 virus pandemic - worldometer. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ 10101998. Available at:
-
- Alsudani R.S.A., Liu J.C. The use of some of the information criterion in determining the best model for forecasting of thalassemia cases depending on Iraqi patient data using ARIMA model. J Appl Math Phys. 2017;5:667–679. doi: 10.4236/jamp.2017.53056. - DOI
-
- De P., Sahu D., Pandey A., Gulati B.K., Chandhiok N., Shukla A.K. Post millennium development goals prospect on child mortality in India: an analysis using autoregressive integrated moving averages (ARIMA) model. Health. 2016;8:1845–1872. doi: 10.4236/health.2016.815176. - DOI
-
- Wang Li Y., Peng B., Zhou R., Zhan C.Y., Liu Z. Mathematical modeling and epidemic prediction of COVID-19 and its significance to epidemic prevention and control measures. Ann Infect Dis Epidemiol. 2020;5(1):1052. 2020.
-
- Chadsuthi S., Modchang C., Lenbury Y., Iamsirithaworn S., Triampo W. Modeling seasonal leptospirosis transmission and its association with rainfall and temperature in Thailand using time-series and ARIMAX analyses. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012;5(7):539–546. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources