MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: Vitamin D and COVID-19
- PMID: 32755992
- PMCID: PMC9494342
- DOI: 10.1530/EJE-20-0665
MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: Vitamin D and COVID-19
Abstract
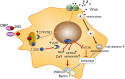
The SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic has generated an explosion of interest both in the mechanisms of infection leading to dissemination and expression of this disease, and in potential risk factors that may have a mechanistic basis for disease propagation or control. Vitamin D has emerged as a factor that may be involved in these two areas. The focus of this article is to apply our current understanding of vitamin D as a facilitator of immunocompetence both with regard to innate and adaptive immunity and to consider how this may relate to COVID-19 disease. There are also intriguing potential links to vitamin D as a factor in the cytokine storm that portends some of the most serious consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection, such as the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Moreover, cardiac and coagulopathic features of COVID-19 disease deserve attention as they may also be related to vitamin D. Finally, we review the current clinical data associating vitamin D with SARS-CoV-2 infection, a putative clinical link that at this time must still be considered hypothetical.
Figures


References
-
- Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Xia J, Zhou X, Xu S, Huang H, Zhang L, Zhou X, Du Cet al. Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Internal Medicine 20201801–11. ( 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994) - DOI - PMC - PubMed

