The Effectiveness of Multi-Session FMT Treatment in Active Ulcerative Colitis Patients: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 32756350
- PMCID: PMC7459721
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8080268
The Effectiveness of Multi-Session FMT Treatment in Active Ulcerative Colitis Patients: A Pilot Study
Abstract
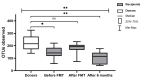
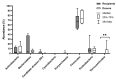
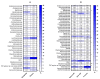
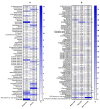
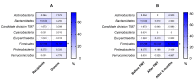
The modification of the microbiome through fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is becoming a very promising therapeutic option for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients. Our pilot study aimed to assess the effectiveness of multi-session FMT treatment in active ulcerative colitis (UC) patients. Ten patients with UC were treated with multi-session FMT (200 mL) from healthy donors, via colonoscopy/gastroscopy. Patients were evaluated as follows: at baseline, at week 7, and after 6 months, routine blood tests (including C reactive protein (CRP) and calprotectin) were performed. 16S rRNA gene (V3V4) sequencing was used for metagenomic analysis. The severity of UC was classified based on the Truelove-Witts index. The assessment of microbial diversity showed significant differences between recipients and healthy donors. FMT contributed to long-term, significant clinical and biochemical improvement. Metagenomic analysis revealed an increase in the amount of Lactobacillaceaea, Micrococcaceae, Prevotellaceae, and TM7 phylumsp.oral clone EW055 during FMT, whereas Staphylococcaceae and Bacillaceae declined significantly. A positive increase in the proportion of the genera Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, Rothia, Streptococcus, and Veillonella and a decrease in Bacillus, Bacteroides, and Staphylococcus were observed based on the correlation between calprotectin and Bacillus and Staphylococcus; ferritin and Lactobacillus, Veillonella, and Bifidobacterium abundance was indicated. A positive change in the abundance of Firmicutes was observed during FMT and after 6 months. The application of multi-session FMT led to the restoration of recipients' microbiota and resulted in the remission of patients with active UC.
Keywords: fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT); gut microbiota; inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); ulcerative colitis (UC).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tomasello G., Bellavia M., Palumbo V.D., Gioviale M.C., Damiani P., Lo Monte A.I. From gut microflora imbalance to mycobacteria infection: Is there a relationship with chronic intestinal inflammatory diseases? Ann. Ital. Di Chir. 2011;82:3613–3668. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

