A reverse-transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for the rapid detection of N gene of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2(SARS-CoV-2)
- PMID: 32758712
- PMCID: PMC7388781
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2020.07.006
A reverse-transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for the rapid detection of N gene of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2(SARS-CoV-2)
Abstract
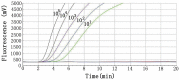
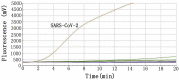
The current outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was reported in China firstly. A rapid, highly sensitive, specific, and simple operational method was needed for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. Here, we established a real-time reverse-transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay (RT-RAA) to detect SARS-CoV-2 rapidly. The primers and probe were designed based on the nucleocapsid protein gene (N gene) sequence of SARS-CoV-2. The detection limit was 10 copies per reaction in this assay, which could be conducted within 15 min at a constant temperature (39 °C), without any cross-reactions with other respiratory tract pathogens, such as other coronaviruses. Furthermore, compared with commercial real-time RT-PCR assay, it showed a kappa value of 0.959 (p < 0.001) from 150 clinical specimens. These results indicated that this real-time RT-RAA assay may be a valuable tool for detecting SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Nucleocapsid protein; Real-time RT-PCR; Real-time RT-RAA; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Chen C., Li X., Li G., Zhao L., Duan S., Yan T., Feng Z., Ma X. Use of a rapid reverse-transcription recombinase aided amplification assay for respiratory syncytial virus detection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018;90:90–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous