Natural Language Processing for Rapid Response to Emergent Diseases: Case Study of Calcium Channel Blockers and Hypertension in the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 32759101
- PMCID: PMC7431235
- DOI: 10.2196/20773
Natural Language Processing for Rapid Response to Emergent Diseases: Case Study of Calcium Channel Blockers and Hypertension in the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Background: A novel disease poses special challenges for informatics solutions. Biomedical informatics relies for the most part on structured data, which require a preexisting data or knowledge model; however, novel diseases do not have preexisting knowledge models. In an emergent epidemic, language processing can enable rapid conversion of unstructured text to a novel knowledge model. However, although this idea has often been suggested, no opportunity has arisen to actually test it in real time. The current coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic presents such an opportunity.
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate the added value of information from clinical text in response to emergent diseases using natural language processing (NLP).
Methods: We explored the effects of long-term treatment by calcium channel blockers on the outcomes of COVID-19 infection in patients with high blood pressure during in-patient hospital stays using two sources of information: data available strictly from structured electronic health records (EHRs) and data available through structured EHRs and text mining.
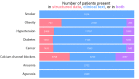
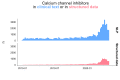
Results: In this multicenter study involving 39 hospitals, text mining increased the statistical power sufficiently to change a negative result for an adjusted hazard ratio to a positive one. Compared to the baseline structured data, the number of patients available for inclusion in the study increased by 2.95 times, the amount of available information on medications increased by 7.2 times, and the amount of additional phenotypic information increased by 11.9 times.
Conclusions: In our study, use of calcium channel blockers was associated with decreased in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 infection. This finding was obtained by quickly adapting an NLP pipeline to the domain of the novel disease; the adapted pipeline still performed sufficiently to extract useful information. When that information was used to supplement existing structured data, the sample size could be increased sufficiently to see treatment effects that were not previously statistically detectable.
Keywords: COVID-19; electronic health records; emergent disease; informatics; medication information; natural language processing; public health; response.
©Antoine Neuraz, Ivan Lerner, William Digan, Nicolas Paris, Rosy Tsopra, Alice Rogier, David Baudoin, Kevin Bretonnel Cohen, Anita Burgun, Nicolas Garcelon, Bastien Rance, AP-HP/Universities/INSERM COVID-19 Research Collaboration; AP-HP COVID CDR Initiative. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (http://www.jmir.org), 14.08.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Snow J. On the Mode of Communication of Cholera. London, UK: Wilson and Ogilvy; 1855.
-
- Chapman W, Dowling J, Ivanov O, Gesteland P, Olszewski R, Espino J, Wagner M. Evaluating natural language processing applications applied to outbreak and disease surveillance. Proceedings of 36th symposium on the interface: computing science and statistics 2004; 36th Symposium on the Interface: Computing Science and Statistics 2004; May 26-29, 2004; Baltimore, MD. 2004.
-
- Zhang L, Sun Y, Zeng H, Peng Y, Jiang X, Shang W, Wu Y, Li S, Zhang Y, Yang L, Chen H, Jin R, Liu W, Li H, Peng K, Xiao G. Calcium channel blocker amlodipine besylate is associated with reduced case fatality rate of COVID-19 patients with hypertension. medRxiv. 2020 Apr 14;:preprint. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.08.20047134. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Devlin J, Chang M, Lee K, Toutanova K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXivcs. 2018. Oct 10, [2018-11-17]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical