Inducers of the endothelial cell barrier identified through chemogenomic screening in genome-edited hPSC-endothelial cells
- PMID: 32759214
- PMCID: PMC7443870
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1911532117
Inducers of the endothelial cell barrier identified through chemogenomic screening in genome-edited hPSC-endothelial cells
Erratum in
-
Correction to Supporting Information for Roudnicky et al., Inducers of the endothelial cell barrier identified through chemogenomic screening in genome-edited hPSC-endothelial cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 15;117(37):23193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2017620117. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32900955 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
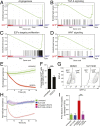
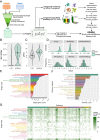
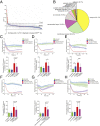
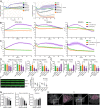
The blood-retina barrier and blood-brain barrier (BRB/BBB) are selective and semipermeable and are critical for supporting and protecting central nervous system (CNS)-resident cells. Endothelial cells (ECs) within the BRB/BBB are tightly coupled, express high levels of Claudin-5 (CLDN5), a junctional protein that stabilizes ECs, and are important for proper neuronal function. To identify novel CLDN5 regulators (and ultimately EC stabilizers), we generated a CLDN5-P2A-GFP stable cell line from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs), directed their differentiation to ECs (CLDN5-GFP hPSC-ECs), and performed flow cytometry-based chemogenomic library screening to measure GFP expression as a surrogate reporter of barrier integrity. Using this approach, we identified 62 unique compounds that activated CLDN5-GFP. Among them were TGF-β pathway inhibitors, including RepSox. When applied to hPSC-ECs, primary brain ECs, and retinal ECs, RepSox strongly elevated barrier resistance (transendothelial electrical resistance), reduced paracellular permeability (fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran), and prevented vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA)-induced barrier breakdown in vitro. RepSox also altered vascular patterning in the mouse retina during development when delivered exogenously. To determine the mechanism of action of RepSox, we performed kinome-, transcriptome-, and proteome-profiling and discovered that RepSox inhibited TGF-β, VEGFA, and inflammatory gene networks. In addition, RepSox not only activated vascular-stabilizing and barrier-establishing Notch and Wnt pathways, but also induced expression of important tight junctions and transporters. Taken together, our data suggest that inhibiting multiple pathways by selected individual small molecules, such as RepSox, may be an effective strategy for the development of better BRB/BBB models and novel EC barrier-inducing therapeutics.
Keywords: CLDN5; chemogenomic library; endothelial cell barrier; genome editing; human pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: This study is supported by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. F. Roudnicky, J.D.Z., B.K.K., N.J.P., Y.L., L.S.-P., H.R., P.S., S.G., M.L., S.U., F. Revelant, O.E., G.S., V.K., K.C., M.T., B.B., M.G., C.P., M.B., C.A.M., and P.D.W. are employees of F. Hoffmann-La Roche. L.D.G. and Z.M. are employees of Genentech Inc. F. Roudnicky, N.J.P., and V.K. were supported by a Roche postdoctoral fellowship. B.K.K. was supported by a Roche doctoral fellowship. C.A.C. is a founder and chief scientific officer of Sana Biotechnology. Neither a reagent nor any funding from Sana Biotechnology was used in this study.
Figures


References
-
- Klaassen I., Van Noorden C. J., Schlingemann R. O., Molecular basis of the inner blood-retinal barrier and its breakdown in diabetic macular edema and other pathological conditions. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 34, 19–48 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

