Exploring the lncRNAs Related to Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Meat Quality Traits in Pigs
- PMID: 32759632
- PMCID: PMC7465969
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11080883
Exploring the lncRNAs Related to Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Meat Quality Traits in Pigs
Abstract
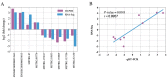
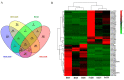
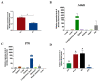
The alteration in skeletal muscle fiber is a critical factor affecting livestock meat quality traits and human metabolic diseases. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a diverse class of non-coding RNAs with a length of more than 200 nucleotides. However, the mechanisms underlying the regulation of lncRNAs in skeletal muscle fibers remain elusive. To understand the genetic basis of lncRNA-regulated skeletal muscle fiber development, we performed a transcriptome analysis to identify the key lncRNAs affecting skeletal muscle fiber and meat quality traits on a pig model. We generated the lncRNA expression profiles of fast-twitch Biceps femoris (Bf) and slow-twitch Soleus (Sol) muscles and identified the differentially expressed (DE) lncRNAs using RNA-seq and performed bioinformatics analyses. This allowed us to identify 4581 lncRNA genes among six RNA libraries and 92 DE lncRNAs between Bf and Sol which are the key candidates for the conversion of skeletal muscle fiber types. Moreover, we detected the expression patterns of lncRNA MSTRG.42019 in different tissues and skeletal muscles of various development stages. In addition, we performed a correlation analyses between the expression of DE lncRNA MSTRG.42019 and meat quality traits. Notably, we found that DE lncRNA MSTRG.42019 was highly expressed in skeletal muscle and its expression was significantly higher in Sol than in Bf, with a positive correlation with the expression of Myosin heavy chain 7 (MYH7) (r = 0.6597, p = 0.0016) and a negative correlation with meat quality traits glycolytic potential (r = -0.5447, p = 0.0130), as well as drip loss (r = -0.5085, p = 0.0221). Moreover, we constructed the lncRNA MSTRG.42019-mRNAs regulatory network for a better understanding of a possible mechanism regulating skeletal muscle fiber formation. Our data provide the groundwork for studying the lncRNA regulatory mechanisms of skeletal muscle fiber conversion, and given the importance of skeletal muscle fiber types in muscle-related diseases, our data may provide insight into the treatment of muscular diseases in humans.
Keywords: RNA-seq; lncRNA; meat quality; metabolic diseases; pig; skeletal muscle fiber.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Reyes N.L., Banks G.B., Tsang M., Margineantu D., Gu H., Djukovic D., Chan J., Torres M., Liggitt H.D., Hirenallur S.D., et al. Fnip1 regulates skeletal muscle fiber type specification, fatigue resistance, and susceptibility to muscular dystrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015;112:424–429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1413021112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Petchey L.K., Risebro C.A., Vieira J.M., Roberts T., Bryson J.B., Greensmith L., Lythgoe M.F., Riley P.R. Loss of Prox1 in striated muscle causes slow to fast skeletal muscle fiber conversion and dilated cardiomyopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:9515–9520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406191111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

