Nuclear Regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling: It's a Complex Situation
- PMID: 32759724
- PMCID: PMC7465203
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11080886
Nuclear Regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling: It's a Complex Situation
Abstract
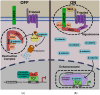
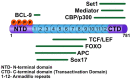
Wnt signaling is an evolutionarily conserved metazoan cell communication pathway required for proper animal development. Of the myriad of signaling events that have been ascribed to cellular activation by Wnt ligands, the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway has been the most studied and best understood. Misregulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling has been implicated in developmental defects in the embryo and major diseases in the adult. Despite the latter, no drugs that inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin pathway have been approved by the FDA. In this review, we explore the least understood step in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway-nuclear regulation of Wnt target gene transcription. We initially describe our current understanding of the importation of β-catenin into the nucleus. We then focus on the mechanism of action of the major nuclear proteins implicated in driving gene transcription. Finally, we explore the concept of a nuclear Wnt enhanceosome and propose a modified model that describes the necessary components for the transcription of Wnt target genes.
Keywords: BCL9; Pygopus; TCF/LEF; TLE; Wnt/β-catenin signaling; enhanceosome; nuclear regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
E.L. and D.J.R. are co-founders of StemSynergy Therapeutics Inc., a company that seeks to develop inhibitors of the Wnt pathway and other pathways for the treatment of cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Cong F., Schweizer L., Varmus H. Wnt signals across the plasma membrane to activate the beta-catenin pathway by forming oligomers containing its receptors, frizzled and LRP. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2004;131:5103–5115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

