HIV Preexposure Prophylaxis and Treatment as Prevention - Beliefs and Access Barriers in Men Who Have Sex With Men (MSM) and Transgender Women: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 32760758
- PMCID: PMC7398630
- DOI: 10.17294/2330-0698.1737
HIV Preexposure Prophylaxis and Treatment as Prevention - Beliefs and Access Barriers in Men Who Have Sex With Men (MSM) and Transgender Women: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Purpose: While the annual rate of new HIV infections and diagnoses has remained stable for most groups, troubling increases are seen in transgender women and racial/ethnic-minority men who have sex with men (MSM), groups that are disproportionately affected by HIV. The primary purpose of this systematic review is to examine factors that impact attitudes and beliefs about preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and treatment as prevention (TasP) and to explore barriers to PrEP uptake in MSM and transgender women.
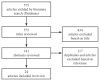
Methods: Using MeSH terms and relevant keywords, we conducted a systematic review of studies published between 2010 and 2019. We searched 4 literature databases and identified studies on MSM and transgender women to elucidate perceptions of PrEP and TasP as well as barriers to access.
Results: The search yielded several prominent themes associated with beliefs about HIV prevention approaches and barriers to PrEP access in MSM and transgender women. One was a lack of awareness or insufficient knowledge of PrEP and TasP. Structural barriers and geographic isolation also prevent access to HIV prevention. Sexual minority and HIV-related stigma, internalized homonegativity, and misinterpretations of messages within HIV prevention campaigns have negatively impacted PrEP uptake and beliefs about PrEP and TasP. Quality of the relationship MSM or transgender people have with their health care provider can facilitate or hinder HIV prevention. Finally, variability in beliefs about the efficacy of TasP has negatively affected the impact of TasP messaging campaigns.
Conclusions: Although there is evidence of increasing PrEP use in at-risk individuals, several barriers prevent wider acceptance and uptake. Misunderstanding about the meaning of "undetectable" and skepticism about the evidence behind TasP messaging campaigns are likely to delay the World Health Organization's stated goal of getting to zero transmissions.
Keywords: HIV; MSM; preexposure prophylaxis; transgender women; treatment as prevention.
© 2020 Aurora Health Care, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest None.
Figures
References
-
- Mustanski B, Ryan DT, Remble TA, D’Aquila RT, Newcomb ME, Morgan E. Discordance of self-report and laboratory measures of HIV viral load among young men who have sex with men and transgender women in Chicago: implications for epidemiology, care, and prevention. AIDS Behav. 2018;22:2360–7. doi: 10.1007/s10461-018-2112-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rodger AJ, Cambiano V, Bruun T, et al. Risk of HIV transmission through condomless sex in serodifferent gay couples with the HIV-positive partner taking suppressive antiretroviral therapy (PARTNER): final results of a multicentre, prospective, observational study. Lancet. 2019;393:2428–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30418-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous