Rapid, random-access, and quantification of hepatitis B virus using the Cepheid Xpert HBV viral load assay
- PMID: 32761911
- PMCID: PMC8247333
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.26392
Rapid, random-access, and quantification of hepatitis B virus using the Cepheid Xpert HBV viral load assay
Abstract
Background: Monitoring viral load (VL) is an essential part of the management of patients chronically infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV). The commercial HBV VL assays currently available are generally performed on high-throughput platforms for batch wise testing of plasma samples, with relatively long turn-around-times. Rapid VL testing could provide immediate input to clinical decision making.
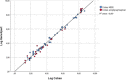
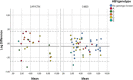
Methods: One hundred two stored plasma samples from 102 patients who were previously tested for HBV VL by the Cobas Ampliprep/Taqman or Cobas 4800 (Roche, Pleasanton, CA), were analyzed by the recently introduced Cepheid Xpert HBV Viral Load Assay. Thirty-one of the 102 samples were negative for HBV DNA and 71 out of 102 samples had a detectable VL. HBV DNA loads ranged from <20 to 5E8 IU/mL. HBV genotypes (A, B, C, D, E, and G) were known for 52 of the VL positive samples. Correlation of VL results between both assays was determined by the Pearson correlation coefficient (r2 ). The level of concordance was assessed using the Bland-Altman analysis.
Results: HBV VLs correlated well between both assays, across all genotypes (Pearson correlation coefficient r2 = 0.987). Six samples exceeded a 0.5 log difference between assays. Bland-Altman analysis demonstrated a mean of the difference of -0.107 log and a standard deviation of 0.271 log.
Conclusion: High correlation was observed between the Roche Cobas HBV Viral Load tests and the Xpert HBV Viral Load Assay, thus enabling rapid, random access, and accurate HBV VL assessment.
Keywords: hepatitis B virus; molecular diagnostics; random-access testing; viral load.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Medical Virology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the contributing authors have any conflicts of interest, except that the cartridges used in the viral load testing of Hepatitis B virus on the GeneXpert instrument System (Cepheid, Sunnyvale, CA) were provided by Cepheid.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Real-world application of the Xpert® HBV viral load assay on serum and dried blood spots.J Med Virol. 2021 Jun;93(6):3707-3713. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26662. Epub 2020 Nov 22. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33174623
-
Analytical performance of the Hologic Aptima HBV Quant Assay and the COBAS Ampliprep/COBAS TaqMan HBV test v2.0 for the quantification of HBV DNA in plasma samples.J Clin Virol. 2018 Jul;104:83-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2018.05.007. Epub 2018 May 18. J Clin Virol. 2018. PMID: 29783147
-
Performance of the Xpert HBV Viral Load assay versus the Aptima Quant assay for quantifying hepatitis B virus DNA.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020 Feb;96(2):114946. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2019.114946. Epub 2019 Nov 16. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31771903
-
Rapid and quantitative detection of hepatitis B virus.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 14;21(42):11954-63. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.11954. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26576084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extended analysis on peripheral blood cytokines correlated with hepatitis B virus viral load in chronically infected patients - a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 31;11:1429926. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1429926. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39149606 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
How Could POCT be a Useful Tool for Migrant and Refugee Health?EJIFCC. 2021 Jun 29;32(2):200-208. eCollection 2021 Jun. EJIFCC. 2021. PMID: 34421489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Hepatitis B Virus Point-of-care DNA Viral Load Testing Compared With Laboratory-based Standard-of-care Approaches on Uptake of HBV Viral Load Testing, Treatment, and Turnaround Times: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 26;11(9):ofae483. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae483. eCollection 2024 Sep. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39296343 Free PMC article.
-
Point-of-Care Tests for Hepatitis B: An Overview.Cells. 2020 Oct 2;9(10):2233. doi: 10.3390/cells9102233. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33023265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time to Initiation of Hepatitis B Treatment is Reduced With the Use of the Xpert HBV Viral Load Kit.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 18;12(5):ofaf238. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaf238. eCollection 2025 May. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40352629 Free PMC article.
-
Tunable Duplex Semiquantitative Detection of Nucleic Acids with a Visual Lateral Flow Immunoassay Readout.Anal Chem. 2022 Mar 8;94(9):3956-3962. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c05039. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35199994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . Global hepatitis report. 2017. https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/
-
- EASL . EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. 2017. - PubMed
-
- Elgouhari HM, Abu‐Rajab Tamimi TI, Carey WD. Hepatitis B virus infection: understanding its epidemiology, course, and diagnosis. Cleve Clin J Med. 2008;75(12):881‐889. - PubMed
-
- Braun P, Delgado R, Drago M, et al. A European multicientre study on the comparison of HBV viral loads between VERIS HBV assay and Roche COBAS((R)) TAQMAN((R)) HBV test, Abbott RealTime HBV assay, Siemens VERSANT HBV assay, and Qiagen artus HBV RG kit. J Clin Virol. 2017;95:76‐83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical