Cabbage and fermented vegetables: From death rate heterogeneity in countries to candidates for mitigation strategies of severe COVID-19
- PMID: 32762135
- PMCID: PMC7436771
- DOI: 10.1111/all.14549
Cabbage and fermented vegetables: From death rate heterogeneity in countries to candidates for mitigation strategies of severe COVID-19
Abstract
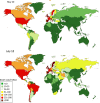
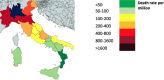
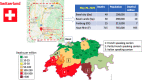
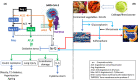
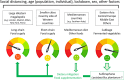
Large differences in COVID-19 death rates exist between countries and between regions of the same country. Some very low death rate countries such as Eastern Asia, Central Europe, or the Balkans have a common feature of eating large quantities of fermented foods. Although biases exist when examining ecological studies, fermented vegetables or cabbage have been associated with low death rates in European countries. SARS-CoV-2 binds to its receptor, the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). As a result of SARS-CoV-2 binding, ACE2 downregulation enhances the angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1 R) axis associated with oxidative stress. This leads to insulin resistance as well as lung and endothelial damage, two severe outcomes of COVID-19. The nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) is the most potent antioxidant in humans and can block in particular the AT1 R axis. Cabbage contains precursors of sulforaphane, the most active natural activator of Nrf2. Fermented vegetables contain many lactobacilli, which are also potent Nrf2 activators. Three examples are: kimchi in Korea, westernized foods, and the slum paradox. It is proposed that fermented cabbage is a proof-of-concept of dietary manipulations that may enhance Nrf2-associated antioxidant effects, helpful in mitigating COVID-19 severity.
Keywords: COVID-19; Lactobacillus; angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; cabbage; diet; fermented vegetable; kimchi; sulforaphane.
© 2020 EAACI and John Wiley and Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley and Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

Comment in
-
Cabbage and COVID-19.Allergy. 2021 Mar;76(3):966-967. doi: 10.1111/all.14654. Allergy. 2021. PMID: 33675254 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Stafford N. Covid‐19: Why Germany's case fatality rate seems so low. BMJ. 2020;369:m1395. - PubMed
-
- Bousquet J, Czarlewski W, Blain H, Zuberbier T, Anto J. Rapid Response: Why Germany’s case fatality rate seems so low: Is nutrition another possibility. BMJ. 2020. https://www.bmj.com/content/369/bmj.m1395/rr‐12
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

