Rapid Implementation of a Diabetes Telemedicine Clinic During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Outbreak: Our Protocol, Experience, and Satisfaction Reports in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 32762362
- PMCID: PMC7925440
- DOI: 10.1177/1932296820947094
Rapid Implementation of a Diabetes Telemedicine Clinic During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Outbreak: Our Protocol, Experience, and Satisfaction Reports in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Background: The importance of telemedicine in diabetes care became more evident during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic as many people with diabetes, especially those in areas without well-established telemedicine, lost access to their health care providers (HCPs) during this pandemic.
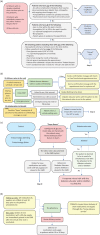
Subjects and methods: We describe a simplified protocol of a Diabetes Telemedicine Clinic that utilizes technological tools readily available to most people with diabetes and clinics around the world. We report the satisfaction of 145 patients and 14 HCPs who participated in the virtual clinic and 210 patients who attended the virtual educational sessions about "Diabetes and Ramadan."
Results: The majority of patients agreed or strongly agreed that the use of telemedicine was essential in maintaining a good glucose control during the pandemic (97%) and they would use the clinic again in the future (86%). A similar high satisfaction was reported by patients who attended the "Diabetes and Ramadan" virtual educational session and 88% of them recommended continuing this activity as a virtual session every year. Majority of the HCPs (93%) thought the clinic protocol was simple and did not require a dedicated orientation session prior to implementing.
Conclusions: The simplicity of our Diabetes Telemedicine Clinic protocol and the high satisfaction reported by patients and HCPs make it a suitable model to be adopted by clinics, especially during pandemics or disasters in resource-limited settings. This clinic model can be quickly implemented and does not require technological tools other than those widely available to most people with diabetes, nowadays. We were able to successfully reduce the number of patients, HCPs, and staff physically present in the clinics during the COVID-19 pandemic without negatively impacting the patients' nor the HCPs' satisfaction with the visits.
Keywords: COVID-19; Saudi Arabia; diabetes; telemedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
The impact of a prolonged lockdown and utilization of diabetes telemedicine on cardiometabolic health in people with diabetes during the COVID-19 outbreak in Saudi Arabia.Prim Care Diabetes. 2022 Oct;16(5):644-649. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2022.06.002. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Prim Care Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 35773134
-
Perception of virtual clinics among Saudi adults with type 1 diabetes during the COVID-19 pandemic.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021 Jul-Aug;15(4):102175. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.06.012. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021. PMID: 34186374 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of telemedicine on patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia: Findings and implications.J Telemed Telecare. 2023 Jun;29(5):390-398. doi: 10.1177/1357633X20985763. Epub 2021 Feb 1. J Telemed Telecare. 2023. PMID: 33525952 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Endocrinology in the Time of COVID-19: Considerations for the Rapid Implementation of Telemedicine and Management of Pediatric Endocrine Conditions.Horm Res Paediatr. 2020;93(6):343-350. doi: 10.1159/000513060. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Horm Res Paediatr. 2020. PMID: 33486483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telemedicine and the Interdisciplinary Clinic Model: During the COVID-19 Pandemic and Beyond.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Oct;163(4):673-675. doi: 10.1177/0194599820932167. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 32484731 Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-19-related knowledge influences mental health, self-care behaviors, and quality of life among elderly with non-communicable diseases in Northern Thailand.Front Public Health. 2022 Oct 28;10:993531. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.993531. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36388338 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare Providers' Experience with Saudi Arabia's 937 Virtual Medical Call Centers and Telehealth.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Jun 22;17:2949-2960. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S467172. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 38933694 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection in multiple sclerosis patients: interaction with treatments, adjuvant therapies, and vaccines against COVID-19.J Neurol. 2022 Sep;269(9):4581-4603. doi: 10.1007/s00415-022-11237-1. Epub 2022 Jul 5. J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35788744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cost-effectiveness of telemedicine care for patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2021 Sep 8;12:20406223211042542. doi: 10.1177/20406223211042542. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2021. PMID: 34729144 Free PMC article.
-
A qualitative study on strategies to enhance diabetes Internet-based nursing clinic services from the perspective of patients in China.BMC Nurs. 2025 Mar 12;24(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-02925-0. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40075400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re.... Accessed April 22, 2020.
-
- Ministry of Health. MOH News - MOH reports first case of coronavirus infection. https://www.moh.gov.sa/en/Ministry/MediaCenter/News/Pages/News-2020-03-0.... Accessed April 22, 2020.
-
- Wamsley L. Life during coronavirus: what different countries are doing to stop the spread. The Coronavirus Crisis; 2020. https://www.npr.org/sections/goatsandsoda/2020/03/10/813794446/life-duri.... Accessed April 22, 2020.
-
- Saudi Press Agency. Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques issues curfew order to limit spread of Novel Coronavirus from seven in the evening until six in the morning for 21 days starting in the evening of Monday 23 March. https://www.spa.gov.sa/2050402. Accessed April 22, 2020.
-
- Ministry of Health. MOH News - COVID-19 follow-up committee reviews latest updates of the fight against the pandemic. https://www.moh.gov.sa/en/Ministry/MediaCenter/News/Pages/News-2020-03-2.... Accessed April 22, 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

