Multifunctional biomimetic hydrogel systems to boost the immunomodulatory potential of mesenchymal stromal cells
- PMID: 32763614
- PMCID: PMC7477339
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120266
Multifunctional biomimetic hydrogel systems to boost the immunomodulatory potential of mesenchymal stromal cells
Abstract
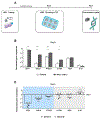
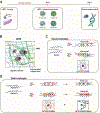
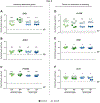
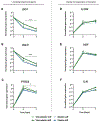
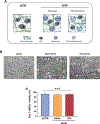
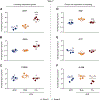
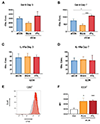
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) hold great therapeutic potential, in part because of their immunomodulatory properties. However, these properties can be transient and depend on multiple factors. Here, we developed a multifunctional hydrogel system to synergistically enhance the immunomodulatory properties of MSCs, using a combination of sustained inflammatory licensing and three-dimensional (3D) encapsulation in hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties. The immunomodulatory extracellular matrix hydrogels (iECM) consist of an interpenetrating network of click functionalized-alginate and fibrillar collagen, in which interferon γ (IFN-γ) loaded heparin-coated beads are incorporated. The 3D microenvironment significantly enhanced the expression of a wide panel of pivotal immunomodulatory genes in bone marrow-derived primary human MSCs (hMSCs), compared to two-dimensional (2D) tissue culture. Moreover, the inclusion of IFN-γ loaded heparin-coated beads prolonged the expression of key regulatory genes upregulated upon licensing, including indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) and galectin-9 (GAL9). At a protein level, iECM hydrogels enhanced the secretion of the licensing responsive factor Gal-9 by hMSCs. Its presence in hydrogel conditioned media confirmed the correct release and diffusion of the factors secreted by hMSCs from the system. Furthermore, co-culture of iECM-encapsulated hMSCs and activated human T cells resulted in suppressed proliferation, demonstrating direct regulation on immune cells. These data highlight the potential of iECM hydrogels to enhance the immunomodulatory properties of hMSCs in cell therapies.
Keywords: Alginate; Extracellular matrix; Hydrogel; Immunomodulation; Interferon; MSCs.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stromal cells encapsulated in licensing hydrogels exert delocalized systemic protection against ulcerative colitis via subcutaneous xenotransplantation.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2022 Mar;172:31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2022.01.007. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2022. PMID: 35074553
-
IFN-γ-tethered hydrogels enhance mesenchymal stem cell-based immunomodulation and promote tissue repair.Biomaterials. 2019 Nov;220:119403. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119403. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Biomaterials. 2019. PMID: 31401468 Free PMC article.
-
MSC-derived immunomodulatory extracellular matrix functionalized electrospun fibers for mitigating foreign-body reaction and tendon adhesion.Acta Biomater. 2021 Oct 1;133:280-296. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.04.035. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33894349
-
Enhancing Immunomodulatory Function of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells by Hydrogel Encapsulation.Cells. 2024 Jan 23;13(3):210. doi: 10.3390/cells13030210. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38334602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased Paracrine Immunomodulatory Potential of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Three-Dimensional Culture.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2016 Aug;22(4):322-9. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2015.0532. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2016. PMID: 26861485 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of Inflammation and Its Resolution in Disease and Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 14;23(18):10719. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810719. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetic Acid Enables Precise Tailoring of the Mechanical Behavior of Protein-Based Hydrogels.Nano Lett. 2022 Sep 14;22(17):6942-6950. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c01558. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Nano Lett. 2022. PMID: 36018622 Free PMC article.
-
Viscoelastic Biomaterials for Tissue Regeneration.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2022 Jul;28(7):289-300. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2022.0040. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2022. PMID: 35442107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A multifunctional micropore-forming bioink with enhanced anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.Biofabrication. 2022 Mar 11;14(2):10.1088/1758-5090/ac5936. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/ac5936. Biofabrication. 2022. PMID: 35226880 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-tuning licensing strategies to boost MSC-based immunomodulatory secretome.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Apr 17;16(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04315-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40247371 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benkhoucha M, Santiago-Raber ML, Schneiter G, Chofflon M, Funakoshi H, Nakamura T, Lalive PH, Hepatocyte growth factor inhibits CNS autoimmunity by inducing tolerogenic dendritic cells and CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107 (2010)6424–6429. 10.1073/pnas.0912437107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Spaggiari GM, Capobianco A, Abdelrazik H, Becchetti F, Mingari MC, Moretta L, Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit natural killer-cell proliferation, cytotoxicity, and cytokine production: role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and prostaglandin E2, Blood. 111 (2008) 1327–1333. 10.1182/blood-2007-02-074997. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

