Prevalence of overweight/obesity among the adult population in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32764091
- PMCID: PMC7412611
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039200
Prevalence of overweight/obesity among the adult population in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Overweight and obesity are emerging public health problems in Ethiopia. However, primary study findings on the prevalence of overweight and obesity in Ethiopia are inconsistent. Therefore, this study aimed to estimate the pooled prevalence of overweight and obesity among adults in Ethiopia.
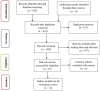
Methods: Studies that looked at overweight and obesity among adults were searched from four international databases. The search involved articles published from 1 January 2010 to 10 March 2020. The Cochran's Q χ2 and the I2 test statistics were used to check heterogeneity among the studies. The funnel plot and Egger's regression tests were also used to assess the presence of publication bias. Subgroup analysis was performed by residence, study setting, sample size and year of study. Sensitivity analysis was also done to assess the effect of a single study on the pooled estimates. Data analysis was done using STATA V.14 software program.
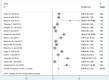
Results: A total of 16 studies with 19 527 study participants were included in this systematic review and meta-analysis. The estimated pooled prevalence of overweight among adults in Ethiopia was 20.4%, and after adjustment for publication bias with the trim-and-fill analysis, the estimated prevalence rate was changed to 19%. Besides, the estimated pooled prevalence of obesity was 5.4%. The prevalence of overweight was higher, 22.6% in studies published since 2015, 22.4% in studies conducted only in urban settings and 24.4% in studies with small sample size (≤384 participants). Similarly, the prevalence of obesity was 6.9% in studies published since 2015, 6.2% in studies conducted only in urban settings, 6.4% in institution-based settings and 9.6% in studies with small sample size.
Conclusion: The prevalence of overweight and obesity is high in Ethiopia compared with previous studies. This needs large scale awareness creation campaigns and situation-based and context-specific prevention strategies.
Keywords: nutrition & dietetics; nutritional support; public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures









References
-
- Fanzo J, Hawkes C, Udomkesmalee E, et al. Global nutrition report: shining a light to Spur action on nutrition, 2018.
-
- World Health organization Global database on body mass index.BMI classification. Geneva: WHO, 2004.
-
- Dobbs R, Sawers C, Thompson F, et al. Overcoming obesity: an initial economic analysis. 2014. McKinsey & Company, 2014: 1–106. wwwmckinseycom/mgi
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
