The Sphingosine Kinase 1 Inhibitor, PF543, Mitigates Pulmonary Fibrosis by Reducing Lung Epithelial Cell mtDNA Damage and Recruitment of Fibrogenic Monocytes
- PMID: 32764262
- PMCID: PMC7460639
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21165595
The Sphingosine Kinase 1 Inhibitor, PF543, Mitigates Pulmonary Fibrosis by Reducing Lung Epithelial Cell mtDNA Damage and Recruitment of Fibrogenic Monocytes
Abstract
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic disease for which novel approaches are urgently required. We reported increased sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) in IPF lungs and that SPHK1 inhibition using genetic and pharmacologic approaches reduces murine bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. We determined whether PF543, a specific SPHK1 inhibitor post bleomycin or asbestos challenge mitigates lung fibrosis by reducing mitochondrial (mt) DNA damage and pro-fibrotic monocyte recruitment-both are implicated in the pathobiology of pulmonary fibrosis. Bleomycin (1.5 U/kg), crocidolite asbestos (100 µg/50 µL) or controls was intratracheally instilled in Wild-Type (C57Bl6) mice. PF543 (1 mg/kg) or vehicle was intraperitoneally injected once every two days from day 7-21 following bleomycin and day 14-21 or day 30-60 following asbestos. PF543 reduced bleomycin- and asbestos-induced pulmonary fibrosis at both time points as well as lung expression of profibrotic markers, lung mtDNA damage, and fibrogenic monocyte recruitment. In contrast to human lung fibroblasts, asbestos augmented lung epithelial cell (MLE) mtDNA damage and PF543 was protective. Post-exposure PF543 mitigates pulmonary fibrosis in part by reducing lung epithelial cell mtDNA damage and monocyte recruitment. We reason that SPHK1 signaling may be an innovative therapeutic target for managing patients with IPF and other forms of lung fibrosis.
Keywords: SPHK1; alveolar epithelial cell; monocytes; mtDNA damage; oxidative stress; pulmonary fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

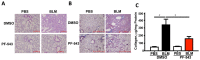

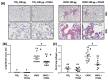
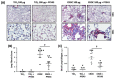
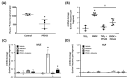
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- I01 CX001777/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- 2IO1BX000786-05A2/United States Veterans Administration
- HL 126609/National Institutes of Health/ HLBI (Project 3)
- P01 AG049665/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5R21AG060211-02/National Institute of Health
- P30-CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 Hl 060678/National Institutes of Health/HLBI (Project 4)
- RO1 HL127342/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134800/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL060678/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG060211/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL126609/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

