Bibliometric Profile of Global Microplastics Research from 2004 to 2019
- PMID: 32764298
- PMCID: PMC7459863
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17165639
Bibliometric Profile of Global Microplastics Research from 2004 to 2019
Abstract
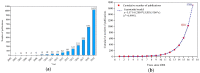
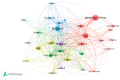
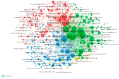
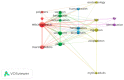
Microplastics (MPs) have generated worldwide attention due to their global distribution in the environment, and their potential harmful effects on human and animal health. To analyze MPs-related scientific publications from a global point of view, we created a bibliometric profile, by searching the Web of Science Core Collection database for the topic "microplastic* or (micro near/1 plastic*)", in publications dated from 2004 to 2019. The results revealed an increasing trend in publication output, and identified contributions of different countries and their collaborations, as well as influential authors and productive journals in the field of MPs research. Using co-citation network analysis in VOSviewer, we mined cited references for knowledge bases about analytical methods, potential sources and spatial distributions of MPs, the impacts of MPs on organisms, and the interaction of MPs with contaminants, as well as microorganisms. We also identified four global hotspots for MPs related research, using author keywords co-occurrence network analysis of all extracted publications, as well as Essential Science Indicators highly cited papers from Clarivate Analytics. Results of this study provide a valuable reference for ongoing MPs-related research, which may be of intrigue and awesome noteworthiness for relevant researchers.
Keywords: VOSviewer software; bibliometric; microplastics; network analysis; research hotspots.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

