Megakaryocytes and platelet-fibrin thrombi characterize multi-organ thrombosis at autopsy in COVID-19: A case series
- PMID: 32766543
- PMCID: PMC7316051
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100434
Megakaryocytes and platelet-fibrin thrombi characterize multi-organ thrombosis at autopsy in COVID-19: A case series
Abstract
Background: There is increasing recognition of a prothrombotic state in COVID-19. Post-mortem examination can provide important mechanistic insights.
Methods: We present a COVID-19 autopsy series including findings in lungs, heart, kidneys, liver, and bone, from a New York academic medical center.
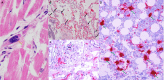
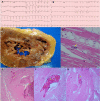
Findings: In seven patients (four female), regardless of anticoagulation status, all autopsies demonstrated platelet-rich thrombi in the pulmonary, hepatic, renal, and cardiac microvasculature. Megakaryocytes were seen in higher than usual numbers in the lungs and heart. Two cases had thrombi in the large pulmonary arteries, where casts conformed to the anatomic location. Thrombi in the IVC were not found, but the deep leg veins were not dissected. Two cases had cardiac venous thrombosis with one case exhibiting septal myocardial infarction associated with intramyocardial venous thrombosis, without atherosclerosis. One case had focal acute lymphocyte-predominant inflammation in the myocardium with no virions found in cardiomyocytes. Otherwise, cardiac histopathological changes were limited to minimal epicardial inflammation (n = 1), early ischemic injury (n = 3), and mural fibrin thrombi (n = 2). Platelet-rich peri‑tubular fibrin microthrombi were a prominent renal feature. Acute tubular necrosis, and red blood cell and granular casts were seen in multiple cases. Significant glomerular pathology was notably absent. Numerous platelet-fibrin microthrombi were identified in hepatic sinusoids. All lungs exhibited diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) with a spectrum of exudative and proliferative phases including hyaline membranes, and pneumocyte hyperplasia, with viral inclusions in epithelial cells and macrophages. Three cases had superimposed acute bronchopneumonia, focally necrotizing.
Interpretation: In this series of seven COVID-19 autopsies, thrombosis was a prominent feature in multiple organs, in some cases despite full anticoagulation and regardless of timing of the disease course, suggesting that thrombosis plays a role very early in the disease process. The finding of megakaryocytes and platelet-rich thrombi in the lungs, heart and kidneys suggests a role in thrombosis.
Funding: None.
Keywords: “Autopsy”; “COVID-19″; “Megakaryocyte”; “Thrombosis”.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Rapkiewicz, Dr. Mai, Dr. Pittaluga, Dr. Thomas, Dr. Kleiner, Dr. Adler and Dr. Gasmi have nothing to disclose. Dr. Carsons reports grants from Novartis and grants from GSK, outside the submitted work. Dr. Berger reports grants from National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, during the conduct of the study; grants from Astrazeneca, other from Jannsen, other from Amgen, outside the submitted work. Dr. Charytan reports personal fees from PLC Medical, grants from bioporto, personal fees from Merck, grants and personal fees from NovoNordisk, grants and personal fees from Jannssen, grants and personal fees from Gilead, personal fees from AstraZeneca, grants and personal fees from Medtronic, grants and personal fees from Amgen, personal fees from Fresenius, personal fees from GSK, outside the submitted work. Dr. Hochman was supported in part by the NYU CTSA grant UL1TR001445, from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) during the conduct of the study; grants from NHLBI, other from AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LLC, other from Arbor Pharmaceuticals LLC, non-financial support from Abbott Vascular, non-financial support from Medtronic Inc, non-financial support from St. Jude Medical Inc, non-financial support from Volcano Corp, non-financial support from Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp, non-financial support from Omron Healthcare Inc, non-financial support from Amgen Inc, outside the submitted work. Dr. Reynolds reports non-financial support from Abbott Vascular, non-financial support from Siemens, non-financial support from Biotelemetry Inc outside the submitted work.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

