Preadmission Diabetes-Specific Risk Factors for Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Diabetes and Coronavirus Disease 2019
- PMID: 32769128
- PMCID: PMC7510015
- DOI: 10.2337/dc20-1543
Preadmission Diabetes-Specific Risk Factors for Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Diabetes and Coronavirus Disease 2019
Abstract
Objective: To examine whether HbA1c, outpatient diabetes treatment regimen, demographics, and clinical characteristics are associated with mortality in hospitalized patients with diabetes and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Research design and methods: This was a retrospective cohort analysis of patients with diabetes hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19 infection from 11 March to 7 May 2020 at a large academic medical center in New York City. Multivariate modeling was used to assess the independent association of HbA1c levels and outpatient diabetes treatment regimen with mortality, in addition to independent effects of demographic and clinical characteristics.
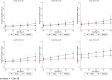
Results: We included 1,126 hospitalized patients with diabetes and COVID-19 for analysis, among whom mean age was 68 years, 50% were male, 75% were Black, mean BMI was 30 kg/m2, 98% had type 2 diabetes, mean HbA1c was 7.5%, and 33.1% died. HbA1c levels were not associated with mortality in unadjusted or adjusted analyses, but an outpatient regimen with any insulin treatment was strongly predictive. Additionally, age, sex, and BMI interacted such that in all age categories, mortality was higher with increasing BMI in males compared with females.
Conclusions: In this large U.S. cohort of hospitalized patients with diabetes and COVID-19, insulin treatment, as a possible proxy for diabetes duration, and obesity rather than long-term glycemic control were predictive of mortality. Further investigation of underlying mechanisms of mortality and inpatient glycemic control is needed.
© 2020 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization WHO Timeline-COVID-19. WHO Newsroom, 2020. Accessed 22 June 2020. Available from https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/29-06-2020-covidtimeline
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2019;157:107843. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous