Reinventing the wheel with a synthetic plant inflammasome
- PMID: 32769206
- PMCID: PMC7456125
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2013380117
Reinventing the wheel with a synthetic plant inflammasome
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
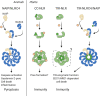
Comment on
-
Induced proximity of a TIR signaling domain on a plant-mammalian NLR chimera activates defense in plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 4;117(31):18832-18839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2001185117. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32709746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jones J. D. G., Vance R. E., Dangl J. L., Intracellular innate immune surveillance devices in plants and animals. Science 354, aaf6395 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Cooper M. D., Alder M. N., The evolution of adaptive immune systems. Cell 124, 815–822 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Zhang X., Dodds P. N., Bernoux M., What do we know about NOD-like receptors in plant immunity? Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 55, 205–229 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

