Plasmid DNA gene therapy of the Niemann-Pick C1 mouse with transferrin receptor-targeted Trojan horse liposomes
- PMID: 32770132
- PMCID: PMC7414904
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-70290-w
Plasmid DNA gene therapy of the Niemann-Pick C1 mouse with transferrin receptor-targeted Trojan horse liposomes
Abstract
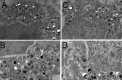
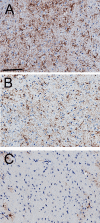
Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) is a lysosomal cholesterol storage disorder, that severely affects the brain, and is caused by mutations in the NPC1 gene, which encodes an intracellular membrane transporter of non-esterified cholesterol. Therapeutic options for NPC1 are few, and classical enzyme replacement therapy with the recombinant protein is not possible as the NPC1 gene product is an insoluble membrane protein, which increases the need for development of gene therapy for NPC1. While viral based gene therapy is under development, it is important to investigate alternative approaches to brain gene therapy without viral vectors. The present work develops a plasmid DNA approach to gene therapy of NPC1 using Trojan horse liposomes (THLs), wherein the plasmid DNA is encapsulated in 100 nm pegylated liposomes, which are targeted to organs with a monoclonal antibody against the mouse transferrin receptor. THLs were encapsulated with a 8.0 kb plasmid DNA encoding the 3.9 kb human NPC1 open reading frame, under the influence of a 1.5 kb platelet derived growth factor B (PDGFB) promoter. THLs were administered weekly beginning at 6-7 weeks in the NPC1-/- null mouse, and delivery of the plasmid DNA, and NPC1 mRNA expression in brain, spleen, and liver were confirmed by quantitative PCR. THL treatment reduced tissue inclusion bodies in brain, and peripheral organs, but did not prolong lifespan in these mice. The work suggests that early treatment after birth may be required to reverse this disease model with NPC1 gene replacement therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
D.J., H.L, and W.M.P. were employees of The Lipogene Company, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Lyoprotectant Optimization for the Freeze-Drying of Receptor-Targeted Trojan Horse Liposomes for Plasmid DNA Delivery.Mol Pharm. 2020 Jun 1;17(6):2165-2174. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00310. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32315188
-
Near complete rescue of experimental Parkinson's disease with intravenous, non-viral GDNF gene therapy.Pharm Res. 2009 May;26(5):1059-63. doi: 10.1007/s11095-008-9815-9. Epub 2008 Dec 23. Pharm Res. 2009. PMID: 19104914
-
A Novel Small NPC1 Promoter Enhances AAV-Mediated Gene Therapy in Mouse Models of Niemann-Pick Type C1 Disease.Cells. 2023 Jun 13;12(12):1619. doi: 10.3390/cells12121619. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37371089 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomal enzyme replacement of the brain with intravenous non-viral gene transfer.Pharm Res. 2008 Feb;25(2):400-6. doi: 10.1007/s11095-007-9357-6. Epub 2007 Jun 30. Pharm Res. 2008. PMID: 17602284
-
Brain Delivery of Nanomedicines: Trojan Horse Liposomes for Plasmid DNA Gene Therapy of the Brain.Front Med Technol. 2020 Nov 16;2:602236. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2020.602236. eCollection 2020. Front Med Technol. 2020. PMID: 35047884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual-Targeting and Stimuli-Triggered Liposomal Drug Delivery in Cancer Treatment.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021 Jun 1;4(3):1028-1049. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00066. eCollection 2021 Jun 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 34151199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes as an Emerging Plasmid Delivery Vehicle for Gene Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 27;15(7):1832. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071832. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organ Weights in NPC1 Mutant Mice Partly Normalized by Various Pharmacological Treatment Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 29;24(1):573. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010573. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614015 Free PMC article.
-
A Historical Review of Brain Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 16;14(6):1283. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061283. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Based HIF1α Gene Therapy Reduces Myocardial Scar and Enhances Angiopoietic Proteome, Transcriptomic and miRNA Expression in Experimental Chronic Left Ventricular Dysfunction.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 May 12;10:767985. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.767985. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35646882 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

