Erythropoietin prevents necrotizing enterocolitis in very preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 32771013
- PMCID: PMC7414749
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-020-02459-w
Erythropoietin prevents necrotizing enterocolitis in very preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is one of the most severe complications in very preterm infants, but there are currently no accepted methods to prevent NEC. Studies have shown that erythropoietin (EPO) has the potential to prevent NEC or improve outcomes of preterm NEC. This study aimed to determine whether recombinant human EPO (rhEPO) could protect against NEC in very preterm infants.
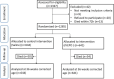
Methods: The study was a prospective randomized clinical trial performed among four NICU centers. A total of 1327 preterm infants with gestational age ≤ 32 weeks were admitted to the centers, and 42 infants were excluded leaving 1285 eligible infants to be randomized to the rhEPO or control group. Infants in the rhEPO group were given 500 IU/kg rhEPO intravenously every other day for 2 weeks, while the control group was given the same volume of saline. The primary outcome was the incidence of NEC in very preterm infants at 36 weeks of corrected gestational age.
Results: A total of 1285 infants were analyzed at 36 weeks of corrected age for the incidence of NEC. rhEPO treatment significantly decreased the incidence of NEC (stage I, II and III) (12.0% vs. 17.1%, p = 0.010), especially confirmed NEC (stage II and III) (3.0% vs. 5.4%, p = 0.027). Meanwhile, rhEPO treatment significantly reduced the number of red blood cells transfusion in the confirmed NEC cases (1.2 ± 0.4 vs. 2.7 ± 1.0, p = 0.004). Subgroup analyses showed that rhEPO treatment significantly decreased the incidence of confirmed NEC at gestational age < 28 weeks (p = 0.019), and the incidence of all stages NEC in preterm infants with hemoglobin < 90 g/l (p = 0.000) and 5 min Apgar score > 5 (p = 0.028).
Conclusion: Repeated low-dose rhEPO treatment is beneficial against NEC in very preterm infants. Trial registration The protocol was registered retrospectively at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03919500) on April 18, 2019. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03919500.
Keywords: Erythropoietin; Necrotizing enterocolitis; Preterm infant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Battersby C, Santhalingam T, Costeloe K, Modi N. Incidence of neonatal necrotising enterocolitis in high-income countries: a systematic review. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2018;103(2):F182–F189. - PubMed
-
- Kastenberg ZJ, Lee HC, Profit J, Gould JB, Sylvester KG. Effect of deregionalized care on mortality in very low-birth-weight infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169(1):26–32. - PubMed
-
- Hintz SR, Kendrick DE, Stoll BJ, Vohr BR, Fanaroff AA, Donovan EF, et al. Neurodevelopmental and growth outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants after necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatrics. 2005;115(3):696–703. - PubMed
-
- Autran CA, Kellman BP, Kim JH, Asztalos E, Blood AB, Spence ECH, et al. Human milk oligosaccharide composition predicts risk of necrotising enterocolitis in preterm infants. Gut. 2018;67(6):1064–1070. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous