2020 Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on Novel Therapies for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee
- PMID: 32771263
- PMCID: PMC7545583
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.037
2020 Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on Novel Therapies for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee
Keywords: ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway; GLP-1RA; SGLT2 inhibitor; atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; cardiovascular risk reduction; diabetes; type 2 diabetes.
Figures
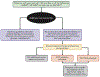
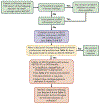

References
-
- Januzzi JL Jr., Ahmad T, Binder LG, et al. 2019 methodology for creating expert consensus decision pathways: a report of the American College of Cardiology. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:1138–50. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care. 2020;43:S111–34. - PubMed
-
- Rawshani A, Rawshani A, Gudbjornsdottir S. Mortality and cardiovascular disease in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:300–1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

