Out-of-focus brain image detection in serial tissue sections
- PMID: 32771371
- PMCID: PMC9475563
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108852
Out-of-focus brain image detection in serial tissue sections
Abstract
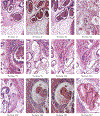
Background: A large part of image processing workflow in brain imaging is quality control which is typically done visually. One of the most time consuming steps of the quality control process is classifying an image as in-focus or out-of-focus (OOF).
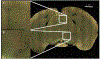
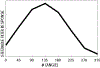
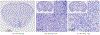
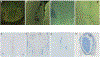
New method: In this paper we introduce an automated way of identifying OOF brain images from serial tissue sections in large datasets (>1.5 PB). The method utilizes steerable filters (STF) to derive a focus value (FV) for each image. The FV combined with an outlier detection that applies a dynamic threshold allows for the focus classification of the images.
Results: The method was tested by comparing the results of our algorithm with a visual inspection of the same images. The results support that the method works extremely well by successfully identifying OOF images within serial tissue sections with a minimal number of false positives.
Comparison with existing methods: Our algorithm was also compared to other methods and metrics and successfully tested in different stacks of images consisting solely of simulated OOF images in order to demonstrate the applicability of the method to other large datasets.
Conclusions: We have presented a practical method to distinguish OOF images from large datasets that include serial tissue sections that can be included in an automated pre-processing image analysis pipeline.
Keywords: Bright-field microscopy; Filters; Fluorescence microscopy; Focus; Image analysis; Image processing; Whole slide imaging.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
None.
Figures



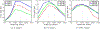
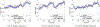
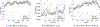

References
-
- Barker J, Hoogi A, Depeursinge A, & Rubin DL (2016). Automated classification of brain tumor type in whole-slide digital pathology images using local representative tiles. Medical image analysis, 30, 60–71. - PubMed
-
- Bohland JW, Wu C, Barbas H, Bokil H, Bota M, Breiter HC, Cline HT, Doyle JC, Freed PJ, Greenspan RJ et al. (2009). A proposal for a coordinated effort for the determination of brainwide neuroanatomical connectivity in model organisms at a mesoscopic scale. PLoS computational biology, 5, e1000334. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bray M-A, & Carpenter A (2017). Imaging Platform, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. Advanced Assay Development Guidelines for Image-Based High Content Screening and Analysis. 2017 Jul 8., In: Sittampalam GS, Grossman A, Brimacombe K, et al., editors. Assay Guidance Manual [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): Eli Lilly and Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; 2004-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK126174/. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

