MRGPRX2 Activation Causes Increased Skin Reactivity in Patients with Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
- PMID: 32771471
- PMCID: PMC11658616
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2020.06.030
MRGPRX2 Activation Causes Increased Skin Reactivity in Patients with Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
Abstract
We present heightened skin reactivity in vivo to two MRGPRX2 drug ligands in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria. Selectivity for the MRGPRX2 pathway by drug ligands was demonstrated by the loss of drug activation in MRGPRX2-KO LAD2 cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement:
None of the authors have any potential financial conflict of interest related to this manuscript.
Figures
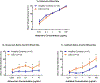
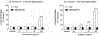
References
-
- Bédard PM, Brunet C, Pelletier G, Hébert J. Increased compound 48/80 induced local histamine release from nonlesional skin of patients with chronic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986;78(6):1121–5. - PubMed
-
- Borici-Mazi R, Kouridakis S, Kontou-Fili K. Cutaneous responses to substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in chronic urticaria: the effect of cetirizine and dimethindene. Allergy. 1999;54(1):46–56. - PubMed
-
- Che D, Rui L, Cao J, Wang J, Zhang Y, Ding Y, et al. Cisatracurium induces mast cell activation and pseudo-allergic reactions via MRGPRX2. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;62:244–50. - PubMed
-
- Fujisawa D, Kashiwakura J, Kita H, Kikukawa Y, Fujitani Y, Sasaki-Sakamoto T, et al. Expression of Mas-related gene X2 on mast cells is upregulated in the skin of patients with severe chronic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134(3):622–33.e9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

